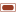
CONCEPT DOMAIN - Outcome centric meta-model (Overview)
| Description | SysFEAT Business-Outcome-Driven Model provides an outcome centric description of the enterprise: 1. Delivered outcomes are shaped to design products (goods & services) that meet customer expectations. 2. Business entities and enabling systems are designed so that: a. outcomes are delivered at a cost/quality ratio. b. enterprise activies are assured against risks and threats 4. Delivered outcomes are monitored to ensure effective product/market fit and continuous improvement. |
|---|---|
| Dictionary |  Dictionary of SysFEAT concepts
Dictionary of SysFEAT concepts |
| Parent Domain | |
| Framework Mapping | SysFEAT Outcome Centric Model |
DOMAIN CONCEPT GRAPH
CONCEPT DESCRIPTIONS
ABSTRACT CONCRETE
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
 Asset Portfolio
Asset Portfolio |
An Asset Portfolio is a Management System aimed at developing and maintaining in operational conditions a set of Mezzo Resource Operating Assets, delivering Resource Capabilitys required by Business Operations. The purpose of Asset Portfolios is efficiency: Managed Resource Assets must provide expected Resource Capabilitys in the best cost / performance ratio. |
 Asset Portfolio Stage
Asset Portfolio Stage |
An Asset Portfolio Stage is a past, current or future state of an Asset Portfolio. Each Asset Portfolio represents an initiative comprising a purposeful set of activities whose primary purpose is focused on achieving a set of clearly defined objectives assigned to assets managed in the Asset Portfolio. It may transcend organisational boundaries and consequently require integrated team working under the direction of a Management Team. |
 Assurance Case
Assurance Case |
An Assurance Case is a claim that a particular enterprise asset or group of Functional Asset adequately mitigates certain identified Risk Types by means of appropriated Control Measures. An Assurance Case shall provide confidence that the concerned assets will function as intended in their environment of use. Privacy Processing Activity(ies), Data Lineages are examples of Assurance Cases .
|
 Assurance Instrument
Assurance Instrument |
An Assurance Instrument is a resource or course of actions used by an Assurance System to achieve its objectives. For instance: Actions plans are course of actions aimed at solving incidents. Data Controls are mechanisms used to ensure data quality and data integrity Privacy Representatives are used to identify national entities in charge of privacy. |
 Assurance System
Assurance System |
An Assurance System is a Management System aimed at ensuring enterprise compliance, resilience, and risk mitigation against both internal and external Policys and threats. It encompasses processes, Directives and technologies that work in concert to validate enterprise adherence to policy requirements, industry standards, and internal policies while simultaneously bolstering the enterprise's ability to withstand and adapt to various challenges and disruptions. ensuring enterprise compliance and resilience against internal and external constraints: a. Regulation constraints: they defined what is allowed and not allowed by the law (See Regulation Article). b. Internal policies and rules constraints: they defined what is allowed and not allowed by the enterprise (see Business Policy). c. Operational constraints: they maintain operational capacities of the company (maintain ability to produce, maintain quality, ensure product development , ability to hire, to train, etc, see Business Rule). d. Architectural constraints: they guide design decisions and shape the overall structure of a system (see Architecture principle). |
 Business Operating Asset
Business Operating Asset |
Business Operating Assets comprise physical assets which contribute to the production and consumption of Business Outcome Events of the enterprise. This includes Business Agent Types, their behaviors (Business Behavior: Business Resource Process, Business Resource Interaction Process), |
 Business Outcome Event
Business Outcome Event |
A Business Outcome Event is a Business Event that signals the happening of a change in the state of a Business Operating Asset, produced by the Business Behavior of a Business Agent Type, for the benefits of an internal or external consumer (especially Customers). |
 Business Process
Business Process |
A Business Process is a set of Business-Process Steps performed by Org-Unit Types and/or by automated systems (Business Systems) to produce a Business Outcome Event. It is depicted as a series of Business-Process Steps, controlled by Business Events and conditions. Business-Process Steps are carried out by the involvment of Org-Unit Types and system resources (often Applications) as participants in the process (Participant Business Agents). During its course of action, a Business Process consumes or produces Business Objects. 1) It may memorize or access Business Objects from its Process Store. 2) It may receive Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Consumption. 3) It may signal the production of Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Production. The course of actions of a Business Process is constrained by the application of rules ( Business Rule Enforcement) that define how to react to what is allowed and not allowed to do,
|
 Business Service Interface
Business Service Interface |
A Business Service Interface is a communication behavior that describes a typical course of interactions intended to produce Business Outcome Events, through the involvement of Business Agent Types. |
 Business System
Business System |
A Business System is a man made artifact (Concrete Hardware System or Business Software System) which exposes Functionalityies and can produce Business Outcome Events. A Business System performs System Processes and participates to System Processes or to Business Processes. In System Processes, a Business System is always an active participant (System Process Participant). In Business Processes, a Business System is either an active participant (Automated Participant) or an Instrument used by Org-Unit Types.
|
 Conceptual Agent
Conceptual Agent |
A Conceptual Agent is an abstract type of Agent Type that depicts a functional division of labor within an enterprise, influencing the formation of its business operating model. The concrete specializations of Conceptual Agent follow the systemic level pattern and come in the form of Operating Domain (a Macro Conceptual Agent) and Business Function (a Mezzo Conceptual Agent).
|
 Conceptual Operating Asset
Conceptual Operating Asset |
A Conceptual Operating Asset is an Operating Asset Type used to describe the Conceptual Operating Model of the enterprise. It includes Value Streams, Operating Domains and Business Functions and the way they contribute to the delivery of Business Outcome Events.
|
 Concrete Hardware System
Concrete Hardware System |
A Concrete Hardware System is a man made tangible artifact which exposes Hardware Capability(ies) and can produce and react to Physical Outcome Events. A Concrete Hardware System performs System Processes and participates to System Processes or to Business Processes. A Concrete Hardware System can embed Computing Systems. Together with its embedded Computing Systems, a Concrete Hardware System can also produce and react to Information Outcome Events. A Concrete Hardware System may be based on a set of Hardware Technology(ies). Examples: - Connected Drone with Online Payment App. - 3D printer. - Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) - Connected fridge providing an ordering Functionality and of course a freezing Hardware Capability. - Production equipment in an assembly line (metal forging machine) - Car
|
 Data Risk Type
Data Risk Type |
A Data Risk Type is a Risk Type that refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data during its entire lifecycle. |
 Enterprise Initiative
Enterprise Initiative |
An Enterprise Initiative is a past, current or future state of the enterprise. Each stage represents an initiative comprising a purposeful set of activities whose primary purpose is focused on achieving a set of clearly defined objectives that may transcend organisational boundaries and consequently require integrated team working under the direction of an Architecture Governance Committee. |
 Functional Asset
Functional Asset |
Functional Assets encompasse all Asset Types used to describe why and how systems operate/function. This includes the Operating Eco-System where system operates to fulfill these purposes (Agent Types and their Behavior Types). Functional Assets include: 1. Blocks defining results of Behavior Types of the enterprise or its sub-systems, that benefit to it internal or external customers : Outcome Event, 2. Blocks used to describe information: Information Asset. 3. Blocks used to describe how the enterprise operates: Operating Asset Types (Agent Type, Behavior Type, Service Interface).
|
 Information Asset
Information Asset |
An Information Asset represents anything that can be communicated or memorized by an Agent Type to produce and react to Outcome Events. An Information Asset is either an Information Entity or an Information Property.
The difference lies in their relationship to change and to time. Information Entity(ies) can change over time and have a lifeycle while Information Propertys are immutable characteristics. |
 Information Domain
Information Domain |
An Information Domain is a family of Information Entity(ies) which constitutes a unit a knowlege required by an Agent Type to operate during Behavior Type execution. |
 Management System
Management System |
A Management System is a mezzo Enduring Initiative within an Enterprise, aimed at creating, maintaining, evaluating, evolving, and operating a collection of essential Functional Architecture Assets of the Enterprise. A Management System may transcend organisational boundaries and consequently requires an integrated team working under the direction of a Management Initiative Committee.
|
 Risk Type
Risk Type |
A Risk Type is a distinct category or classification of risk based on its origin, nature, or potential impact. It helps in organizing and addressing different sources of uncertainty or potential harm that an individual, organization, or system might face. By categorizing risks into different types, entities can develop more targeted mitigation strategies and response plans. Common risk types include Operational Risk Type, Privacy Risk Type, and Compliance Risk Type, among others, |
 Technology System
Technology System |
A Technology System is a Resource Agent Type which produces and reacts to Technology Outcome Events through Technology Interfaces. Technology Systems are enablers of Business Systems. They do not directly deliver Business Outcome Events to internal or external customers. They deliver Technology Outcome Events required by Business Systems to operate. |
SERIALIZATION FORMAT
TEXTUAL SYNTAX RDF
 NIST - Assurance Case
NIST - Assurance Case Martin Fowler - Application Boundary
Martin Fowler - Application Boundary