CONCEPT DOMAIN - Organization & Processes
| Description | The Organization & Processes domain is used to shape how business units operate to deliver the goods and services for which they are responsible. |
|---|---|
| External references |
 Lean.org - Value Stream Mapping Lean.org - Value Stream Mapping
|
| Dictionary |  Dictionary of SysFEAT concepts
Dictionary of SysFEAT concepts |
| Parent Domain |  Business Operations
Business Operations |
| Domain dependencies |  Application Functional Architecture
Application Functional Architecture  EA Pattern - Data Domain
EA Pattern - Data Domain  People & Accountability
People & Accountability  Product & Customer Experience
Product & Customer Experience  SOF - Business Resource Operating Pattern (B-SOF)
SOF - Business Resource Operating Pattern (B-SOF)  SOF - Business System Operating Pattern
SOF - Business System Operating Pattern  System Operating Framework - SOF
System Operating Framework - SOF |
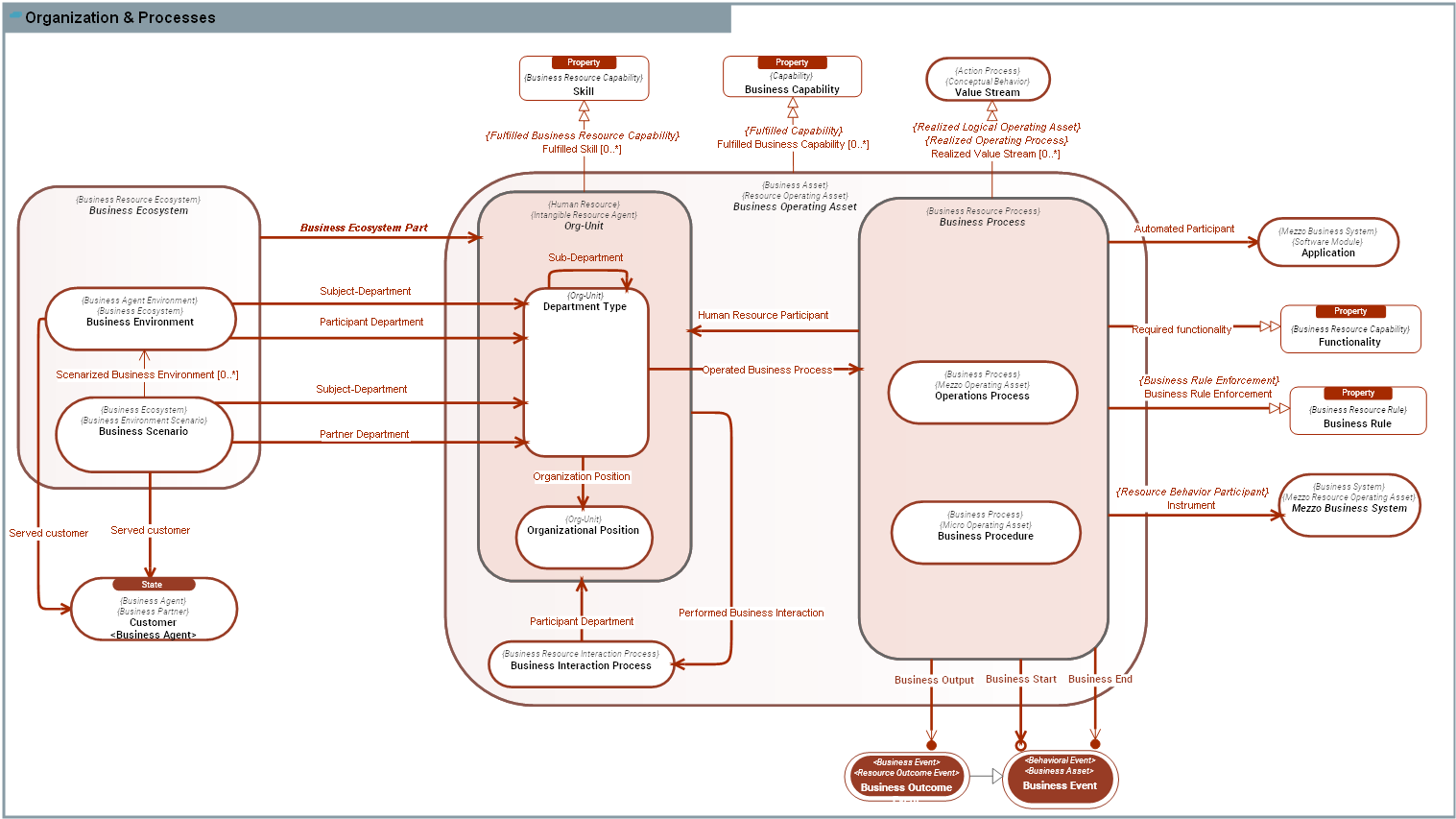
DOMAIN CONCEPT GRAPH
CONCEPT DESCRIPTIONS
ABSTRACT CONCRETE
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
 Business Ecosystem
Business Ecosystem |
A Business Ecosystem is a Business Resource Ecosystem used to describe the operating context in which a Business-Entity (Department Type) exists or lives for a specific purpose. For instance, the Business Ecosystem of a company includes its customers and suppliers. |
 Business Event
Business Event |
A Business Event is a type of business change that is used to coordinate Business Behaviors.
|
 Business Operating Asset
Business Operating Asset |
Business Operating Assets comprise physical assets which contribute to the production and consumption of Business Outcome Events of the enterprise. This includes Business Agent Types, their behaviors (Business Behavior: Business Resource Process, Business Resource Interaction Process), |
 Business Outcome Event
Business Outcome Event |
A Business Outcome Event is a Business Event that signals the happening of a change in the state of a Business Operating Asset, produced by the Business Behavior of a Business Agent Type, for the benefits of an internal or external consumer (especially Customers). |
 Business Process
Business Process |
A Business Process is a set of Business-Process Steps performed by Org-Unit Types and/or by automated systems (Business Systems) to produce a Business Outcome Event. It is depicted as a series of Business-Process Steps, controlled by Business Events and conditions. Business-Process Steps are carried out by the involvment of Org-Unit Types and system resources (often Applications) as participants in the process (Participant Business Agents). During its course of action, a Business Process consumes or produces Business Objects. 1) It may memorize or access Business Objects from its Process Store. 2) It may receive Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Consumption. 3) It may signal the production of Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Production. The course of actions of a Business Process is constrained by the application of rules ( Business Rule Enforcement) that define how to react to what is allowed and not allowed to do,
|
 Mezzo Business System
Mezzo Business System |
A Mezzo Business System is a Business System that corresponds to the mezzo systemic level. Example: |
 Org-Unit Type
Org-Unit Type |
An Org-Unit Type is a type of Human Resource that represent a unit of social groups within an organization, responsible for operating one or more enterprise's Business Functions. |
SERIALIZATION FORMAT
TEXTUAL SYNTAX RDF
 Martin Fowler - Application Boundary
Martin Fowler - Application Boundary