CONCEPT DOMAIN - Application Functional Architecture
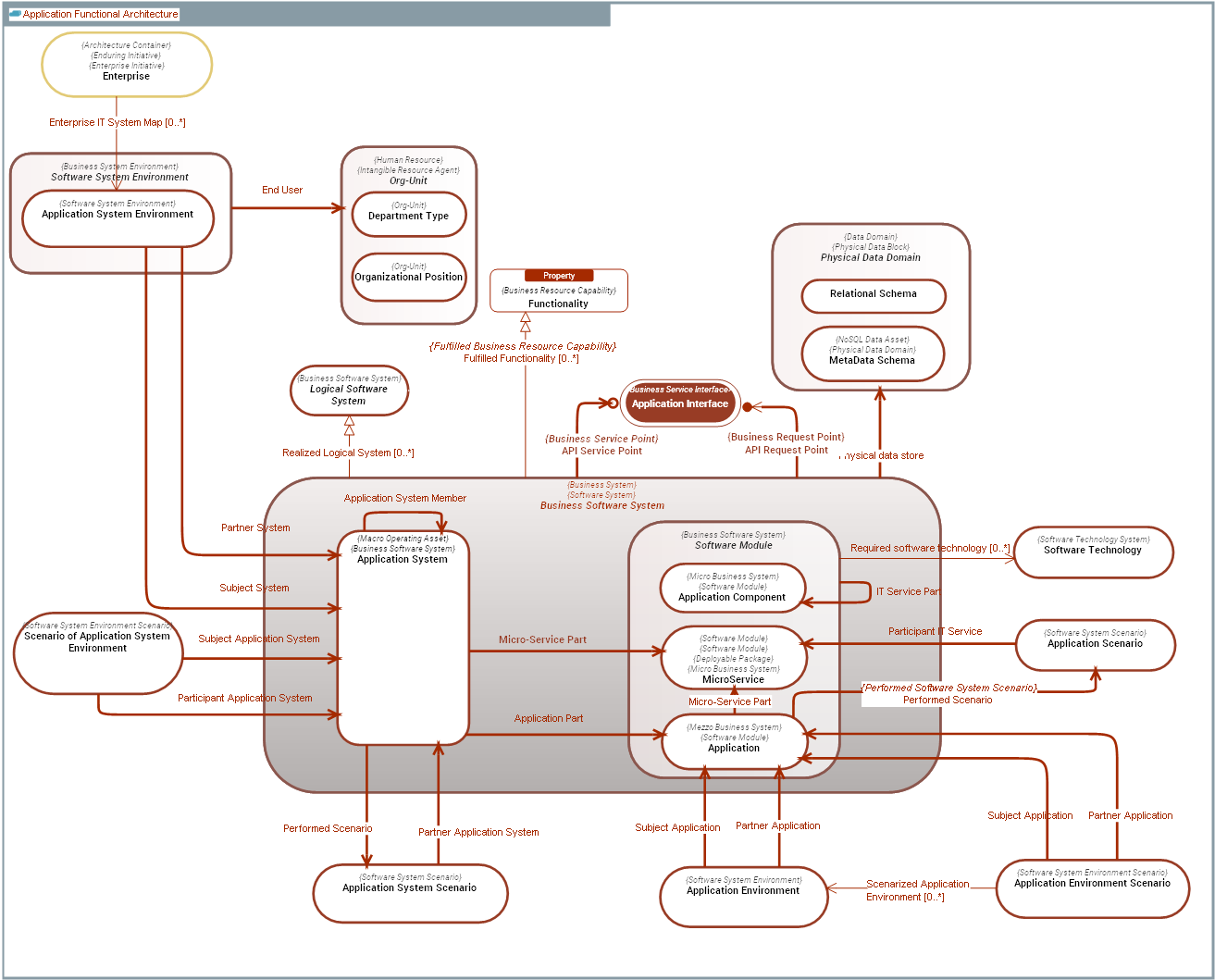
DOMAIN CONCEPT GRAPH
CONCEPT DESCRIPTIONS
ABSTRACT CONCRETE
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
 Business Software System
Business Software System |
A Business Software System is a Business System used by Business Operations, that represents all granularities of software - ranging from MicroServices to enterprise wide Application Systems - used by Business Operations. All Business Software Systems share the following characteristics: 1) They provide Functionalitys. 2) They expose APIs (Application Interfaces) through which they deliver Information Outcome Events. 3) They handle datastores defined by Physical Data Domains. 4) They perform and participate to System Processes.
|
 Logical Software System
Logical Software System |
A Logical Software System is logical specification of a Business Software System, which is independant from the Business Software System physical implementation. For instance, "Human Resource ERP System" is a Logical Application System, while "SAP HR System", "Sage HR System", "Kronos HR System" are Application Systems. |
 Org-Unit Type
Org-Unit Type |
An Org-Unit Type is a type of Human Resource that represent a unit of social groups within an organization, responsible for operating one or more enterprise's Business Functions. |
 Physical Data Domain
Physical Data Domain |
A Physical Data Domain is subset of the metadata of an enterprise’s data store. Each Physical Data Entity in a Physical Data Domain has CRUD characteristics. For instance, the "Client" Table in the "Sales" Physical Data Domain, has all CRUD characteristics. Physical Data Domains define functional data boundaries used both for Data Allocation to Business Systems (see Resource Agent Store) and data governance for data stewardship (see Data Catalog). |
 Software Module
Software Module |
A Software Module is a Business Software System that is part of an application system. All share the ability to be composed of sub-Application Components and have dependencies to enabling Software Technology(ies).
|
 Software System Environment
Software System Environment |
A Software System Environment is an operating context in which a Business Software System defines its interactions with its partners (Partner System) in the form of API connections (Software Connection). It also represents End Users who interact with the system. |
SERIALIZATION FORMAT
TEXTUAL SYNTAX RDF
 C4 Model - Level 1 - System Context Diagram
C4 Model - Level 1 - System Context Diagram Martin Fowler - Application Architecture
Martin Fowler - Application Architecture