IDENTITY - DoDAF Mapping
| Description | Mapping of Dodaf 2 concepts (DM2) to SysFEAT concepts. SysFEAT has a broader set of concepts than DM2 as it also covers the larger scope of Enterprise Architecture, IT Architecture, IT Asset Management, Information Architecture and Operational Assurance. |
|---|---|
| Corresponding SysFEAT Domain | SysFEAT- DoDAF 2 |
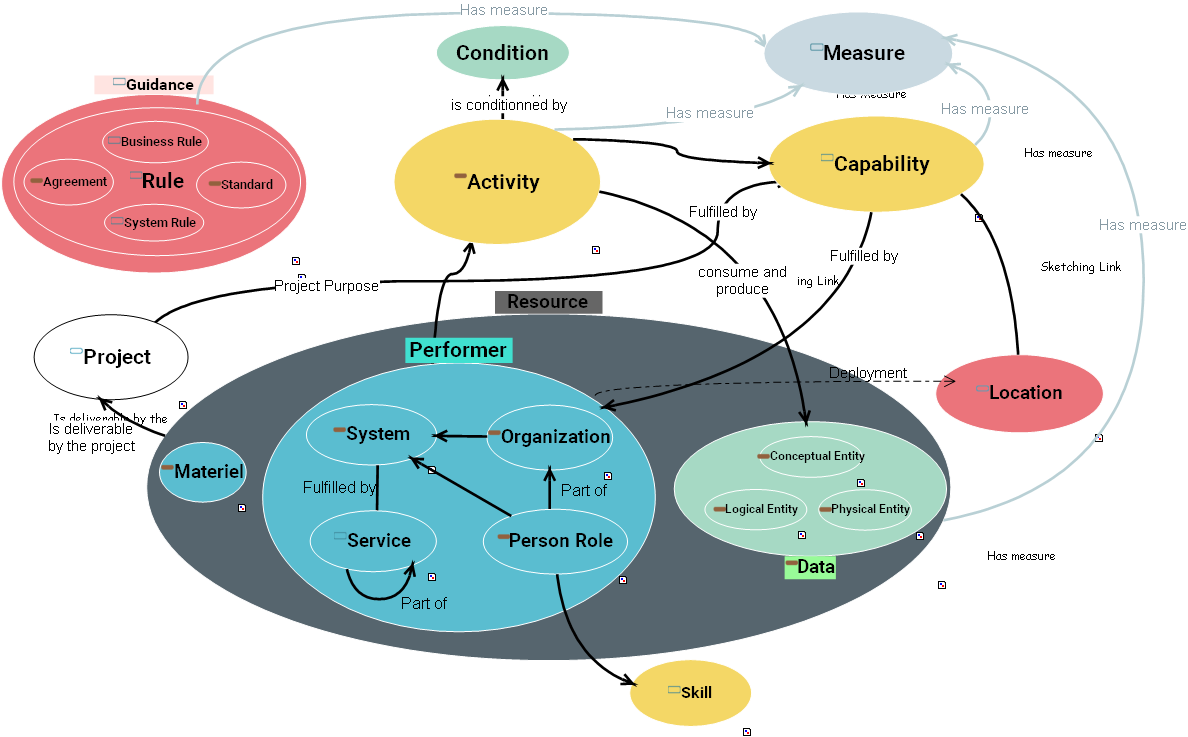
MAPPED ENTITIES
| Framework Concept | Framework Definition | SysFEAT Concept | SysFEAT Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
 Activity Activity |
An Operational Activity is what work is required, specified independently of how it is carried out. To maintain this independence from implementation, logical activities and locations in OV-2 Operational Resource Flow Description are used to represent the structure which carries out the Operational Activities. Operational Activities are realized as System Functions (described in SV-4 Systems Functionality Description) or Service Functions (described in SvcV-4 Services Functionality Description) which are the how to the Operational Activities what, i.e., they are specified in terms of the resources that carry them out.. |  Business Process
Business Process |
A Business Process is a set of Business-Process Steps performed by Org-Units and/or by automated systems (Business Systems) to produce a Business Outcome Event. It is depicted as a series of Business-Process Steps, controlled by Business Events and conditions. Business-Process Steps are carried out by the involvment of Org-Units and system resources (often Applications) as participants in the process (Participant Business Agents). During its course of action, a Business Process consumes or produces Business Objects. 1) It may memorize or access Business Objects from its Process Store. 2) It may receive Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Consumption. 3) It may signal the production of Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Production. The course of actions of a Business Process is constrained by the application of rules ( Business Rule Enforcement) that define how to react to what is allowed and not allowed to do, References: ISO 9000 - 3.4.1 - Process Lean.org - Value Stream Lean.org - Value Stream Mapping OMG - BMM - Business Process OMG - BPMN - Process OMG - UAF - Function OpenGroup - OAA - Process OpenGroup - TOGAF - Enterprise Metamodel Overview OpenGroup - TOGAF 9 - Definition - Process |
 Agreement Agreement |
A consent among parties regarding the terms and conditions of activities that said parties participate in. |  Document
Document |
A Business Document is a document whose lifecycle can be synched to the MEGA repository content: it may be attached to mega objects and a document version bound to a mega object timestamp in the Time Machine. This document can be of any given file format. The Business Document versions are managed within the MEGA repository and the document storage file in the file system can be cyphered. |
 Business Rule Business Rule |
 Business Rule
Business Rule |
A Business Rule is a rule that is under business jurisdiction. A rule’s being under "business jurisdiction" means that it is under the jurisdiction of the community that it governs or guides - that the community can opt to change or discard the rule. Laws of physics may be relevant to an Enterprise; legislation and regulations may be imposed on it; external standards. These things are not Business Rules from the company’s perspective, since it does not have the authority to change them. The company will decide how to react to laws and regulations, and will create Business Rules to ensure compliance with them. Similarly, it will create Business Rules to ensure that standards or best practices are implemented as intended. |
|
 Capability Capability |
The ability to achieve a Desired Effect under specified [performance] standards and conditions through combinations of ways and means [activities and resources] to perform a set of activities. |  Business Capability
Business Capability |
A Business Capability is a conceptual Capability that benefits to Customers (internal or external) of the enterprise. It expresses an ability to produce Conceptual Outcome Events. A Business Capability is defined by its intended Enterprise Outcome Events and the conditions (Condition Property) under which the production of the Enterprise Outcome Events shall be proceeded. The actual Condition Scale Values for a given Business Capability at different stages of Enterprise Initiatives is given by their exhibition (Exhibited Capability). References: OMG - BACM - Capability OMG - UAF - Capability OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Capability OpenGroup - TOGAF - Definition - Business Capability |
 Conceptual Entity Conceptual Entity |
 Concept
Concept |
A Concept is the representation of any tangible or intanglible entity that is of interest to understand the enterprise, its data, resources and activities. A Concept is defined through its essential characteristics which can be: 1) A Concept Property that represents some an immutable factual characteristic such as "name", "amount". 2) A Concept Relationship that represents relationships to other Concepts. References: DDD - Glossary - Entity ISO 15926 - ClassOfInformationObject OMG - SBVR - Concept OMG - UAF - OperationalInformation OpenGroup - TOGAF - Enterprise Metamodel - Business Information OpenGroup -ArchiMate - Business-Object Russell Ackoff - Choice & Communication - Concept |
|
 Condition Condition |
The state of an environment or situation in which a Performer performs. | ||
 Data Data |
Representation of information in a formalized manner suitable for communication, interpretation, or processing by humans or by automatic means. Examples could be whole models, packages, entities, attributes, classes, domain values, enumeration values, records, tables, rows, columns, and fields |  Information Entity
Information Entity |
An Information Entity is an Information Asset that is not fundamentally defined by its attributes, but rather by its continuity. An Information Entity evolves over time and has states. For instance a person is an Information Entity. Employe is a state of a person. An Information Entity has relationships to other Information Entitys and can have Information Propertys. References: DDD - Glossary - Entity |
 Guidance Guidance |
 Directive
Directive |
A Directive is an authoritative declaration that indicates how Agents and their Behaviors should be (or should not be) in the enterprise. Specifically, a Directive defines, constrains or liberates some aspects of an Agent and its Behaviors. As such, Directives shall be considered as constraning Asset Propertys. Directives are intended to assert agent structures or to control or influence their Behaviors. Directives are stated in declarative form. References: OMG - BMM - Directive OMG - SBVR - Element of Guidance OMG - UAF - Rule OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Constraint UCF Glossary - Directive |
|
 Location Location |
A point or extent in space that may be referred to physically or logically. |  Location
Location |
A Location is a geopolitical location anywhere on the earth. Examples: - France - Paris - Washington DC - Cairo - Buenos-Aires - Asia References: ISO 15926 - SpatialLocation OMG - UAF - ActualLocation |
 Logical Entity Logical Entity |
 Logical Data Entity
Logical Data Entity |
A Logical Data Entity is a logical structure of a Data Entity. As any Data Entity, it has an independent existence and can be uniquely identified. A Logical Data Entity is characterized by Logical Relationships it has with other Logical Data Entity(ies) and by its Attributes. References: DDD - Glossary - Entity OMG - UAF - ResourceInformation OpenGroup - TOGAF - Definition - Data Element |
|
 Materiel Materiel |
Equipment, apparatus or supplies that are of interest, without distinction as to its application for administrative or combat purposes. |  Concrete Hardware System
Concrete Hardware System |
A Concrete Hardware System is a man made tangible artifact which exposes Hardware Capability(ies) and can produce and react to Physical Outcome Events. A Concrete Hardware System performs System Processes and participates to System Processes or to Business Processes. A Concrete Hardware System can embed Computing Systems. Together with its embedded Computing Systems, a Concrete Hardware System can also produce and react to Information Outcome Events. A Concrete Hardware System may be based on a set of Hardware Technology(ies). Examples: - Connected Drone with Online Payment App. - 3D printer. - Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) - Connected fridge providing an ordering Functionality and of course a freezing Hardware Capability. - Production equipment in an assembly line (metal forging machine) - Car References: OMG - UAF - System OpenGroup - OAA - Hardware |
 Measure Measure |
 Condition Property
Condition Property |
A Condition Property is a possible value of a Condition Property Type such as a delivery time of 30 minutes, a weight of 20 kg, a high level of confidentiality, stormy conditions. A Condition Property is either a single measure (Measure Property: a weight of 20 kg), an Environmental Property (stormy conditions.) or a Set of Condition Propertiess. Condition Propertys are used to constrain Asset Blocks in the context of non-functional requirement analysis and Value Proposition analysis. Examples: . Cost of 100€ . Delivery time of 30 minutes. . Weight of 20 kg. . Temperature of 18 degree Celcius. |
|
 Organization Organization |
A specific real-world assemblage of people and other resources organized for an on-going purpose. |  Department Type
Department Type |
A Department Type is a Mezzo Org-Unit which serves as an administrative unit template in both government and business Organizations. Examples: - Sales department; - Finance department; - Logistics department.. References: OMG - UAF - Organization OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Business-Actor OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Business-Collaboration OpenGroup - TOGAF - Enterprise Metamodel - Actor Russell Ackoff - System of concepts - FunctionalDivisionOfLabor Russell Ackoff - System of Concepts - Organizations UCF Glossary - Department |
 Performer Performer |
Any entity - human, automated, or any aggregation of human and/or automated - that performs an activity and provides a capability. | ||
 Person Role Person Role |
A category of person roles defined by the role or roles they share that are relevant to an architecture. Includes assigned materiel. |  Organizational Position
Organizational Position |
An Organizational Position is a type of position held by people when part of a Department Type. Examples: - Sales representative - Developer - Storekeeper - Architect References: OMG - UAF - Post OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Business-Actor OpenGroup - TOGAF - Definition - Role UCF Glossary - Position Description |
 Physical Entity Physical Entity |
 Relational Entity
Relational Entity |
A Relational Entity is a relational data structure that is either a Table or a Table View. A Relational Entity is accessible by means of a primary key, and if necessary foreign keys; it is described by an ordered sequence of Columns. References: DDD - Glossary - Entity |
|
 Project Project |
A temporary endeavor undertaken to create Resources or Desired Effects. |  Project
Project |
A Project is a course of action that is being executed or has been selected for execution. An enterprise's Initiatives represent the choices the enterprise has made about how to pursue the change that allows it to achieve its objectives. References: DoDAF2 - Project Viewpoint Martin Fowler - Products over Projects OMG - UAF - ActualProject OpenGroup - TOGAF - Definitions - Work Package |
 Resource Resource |
Data, Information, Performers, Materiel, or Personnel Types that are produced or consumed. | ||
 Rule Rule |
A principle or condition that governs behavior; a prescribed guide for conduct or action. |  Behavioral Rule
Behavioral Rule |
A Behavioral Rule is a Directive intended to guide the Behavior of Agents, in compliance with enterprise Policy(ies) or regulations. Often, a Behavioral Rule is derived from a Policy. Behavioral Rules are enforced in Processes and Agents. References: OMG - BMM - Business Rule OMG - SBVR - Business Rule (Behavioral) |
 Service Service |
A mechanism to enable access to a set of one or more capabilities , where the access is provided using a prescribed interface and is exercised consistent with constraints and policies as specified by the service description. The mechanism is a Performer. The “capabilities” accessed are Resources -- Information, Data, Materiel, Performers, and Geo-political Extents. |  Functionality
Functionality |
A Functionality is a Business Resource Capability offered by Business System Assets (software or hardware) and aimed at delivering Information Outcomes. A Functionality describes WHAT a software or hardware system can provide. Functionality(ies) are used to express the Business System features required by people when performing their job (see Job-to-be-done). For internal customers, these jobs correspond to Business-Process Steps described in Business Process (see Instrument) For enterprise Customers, these jobs correspond to Job-to-be-done in the context of Customer Journeys. References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Capability SAFe© - Feature SAFe© - Features and Capabilities SEBoK - Capability Engineering |
 Skill Skill |
The ability, coming from one's knowledge, practice, aptitude, etc., to do something well. |  Skill
Skill |
A Skill is an ability of a human resource to produce Business Outcome Events. Skills are acquired and refined through training and practice. References: OMG - UAF - Competence OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Capability Wordnet - Skill |
 Standard Standard |
A formal agreement documenting generally accepted specifications or criteria for products, processes, procedures, policies, systems, and/or personnel. |  Standard
Standard |
A standard is definition or format that has been approved by a recognized standards organization or is accepted as a de facto standard by the industry. |
 System System |
A functionally, physically, and/or behaviorally related group of regularly interacting or interdependent elements. |  Application
Application |
An Application is a Business Software System that provides a set of Functionality(ies) that End Users see as a single unit. Essentially Applications are architectural constructions resulting from the combinaison of the following four criteria: 1) A group of Functionality that End Users see as a single unit. 2) A managed asset (Managed Application) associated with a budget line in the context of an Application Portfolio. 3) A body of code that is seen by developers as a single unit. 4) A group of deployable software units (Deployable Application Packages) that must be installed together on one or multiple execution nodes (Computing System). Application is a Mezzo enterprise asset that sits between Application System and Application Component in the decomposition of Business Software Systems. Example: " Payroll" is an Application that is part an " HR System" which is an Application System. The "Payroll" Application includes, among other things, the "Salary and Wage Calculation" Application Component. References: C4 Model - Software System Martin Fowler - Application Boundary Microsoft - Architecture Design - Architecture Styles OMG - UAF - Software OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Component OpenGroup - TOGAF - Definition - Application Component OpenGroup - TOGAF - Enterprise Metamodel - Physical Application Component |
 System Rule System Rule |
 System Rule
System Rule |