IDENTITY - UAF - Motivation
| Description | Identifies and defines motivational elements e.g., challenges, opportunities, and concerns, that pertain to enterprise transformation efforts, and different types of equirements, e.g., operational, services, personnel, resources, or security controls. Recommended Implementation: SysML Block Definition Diagram, SysML Package Diagram, tabular format |
|---|---|
| References | OMG - UAF - View - Motivation |
| Parent Mapping | UAF Mappings |
MAPPED ENTITIES
| Framework Concept | Framework Definition | SysFEAT Concept | SysFEAT Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
 Asset Asset |
An abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be affected by Risk. Asset as applied to Security views is an abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be considered as a subject for security analysis References: OMG - UAF - Asset |
||
 Assurance Case Assurance Case |
The assurance case concept doesn't exist in UAF. It is defined in OMG SCAM specification References: OMG - SACM : AssuranceCasePackage |
 Assurance Case
Assurance Case |
An Assurance Case is a claim that a particular enterprise asset or group of Functional Asset adequately mitigates certain identified Risk Types by means of appropriated Control Measures. An Assurance Case shall provide confidence that the concerned assets will function as intended in their environment of use. Privacy Processing Activity(ies), Data Lineages are examples of Assurance Cases . References: NIST - Assurance Case OMG - SACM : AssuranceCasePackage |
 Operating Asset Type Operating Asset Type |
 Operating Asset Type
Operating Asset Type |
An Operating Asset Type is a Functional Asset that describes the way Outcome Events are produced and consumed: how (Behavior Types) and by whom (Agent Types). Operating Asset Types fulfill Capability(ies) (Fulfilled Capability). As any Functional Architecture Asset, Operating Asset Types are subject to Policy Conformances. In addition, they define Rule Enforcements to indicate how Policy Conformances are met. References: OMG - KerML - Class |
|
 Requirement Requirement |
A Requirement specifies a capability or condition that must (or should) be satisfied. A requirement may specify a function that a system must perform or a performance condition that a system must satisfy. Requirements are used to establish a contract between the customer (or other stakeholder) and those responsible for designing and implementing the system. References: OMG - SysML 1.X - Requirement |
 Requirement
Requirement |
A Requirement is a generic statement used in system engineering to constrain what a Business System Asset should or should not be. The Requirement concept is kept in SysFEAT to maintain compatibility with traditional system engineering methodologies. The preferred approach is to follow capability-based engineering, as promoted by modern enterprise & system architecture (see OMG - UAF - View - Strategic Views) and agile frameworks (see SAFe© - SAFe Requirements Model). References: OMG - SysML 1.X - Requirement SEBoK - Capability Engineering |
 Requirement (Functional) Requirement (Functional) |
Functional requirements are represented by Capability in SysFEAT. |  Capability
Capability |
A Capability is a functional Asset Property which refers to the ability to produce an Outcome Event. Capabilitys are fulfilled by Agent Types performing Action Process Typees and interacting with other Agent Types to produce Outcome Events. References: DAU Glossary - Capability OMG - BACM - Capability OMG - UAF - Capability OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Capability OpenGroup - OAA - Capability OpenGroup - TOGAF - Definition - Capability Russell Ackoff - Choice & Communication - FunctionalClass WordNet - Capability |
 Requirement (Measure) Requirement (Measure) |
Non functional requirements related to qualitative and quantitative aspects are represented by the Condition Scale Value concept in SysFEAT. |  Condition Property
Condition Property |
A Condition Property is a possible value of a Condition Property Type such as a delivery time of 30 minutes, a weight of 20 kg, a high level of confidentiality, stormy conditions. A Condition Property is either a single measure (Measure Property: a weight of 20 kg), an Environmental Property (stormy conditions.) or a Set of Condition Propertiess. Condition Propertys are used to constrain Asset Blocks in the context of non-functional requirement analysis and Value Proposition analysis. Examples: . Cost of 100€ . Delivery time of 30 minutes. . Weight of 20 kg. . Temperature of 18 degree Celcius. |
 Requirement (Policy) Requirement (Policy) |
Non functional requirements related to constraints and guidance are represented by Policy in SysFEAT. Policies range from Regulation Articles, Business Policys to Architecture principles. |
 Policy
Policy |
A Policy is a Directive that is not directly enforceable whose purpose is to govern, guide or constrain the structure and Behavior Type of Agent Types in the enterprise. Policies provide the basis for rules and govern Behavior Types carried out by Agent Types. References: OMG - BMM - Business Policy OMG - UAF - Rule |
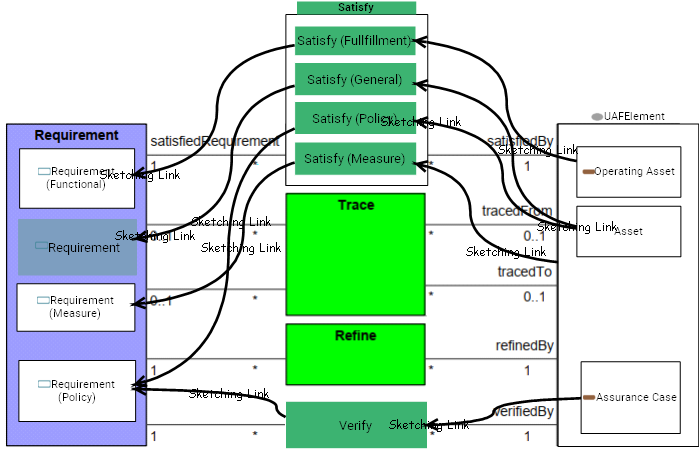
 Satisfy Satisfy |
A Satisfy relationship is a dependency between a requirement and a model element that fulfills the requirement. As with other dependencies, the arrow direction points from the satisfying (client) model element to the (supplier) requirement that is satisfied. | ||
 Satisfy (Fullfillment) Satisfy (Fullfillment) |
Satisfy relationship that is fulfillement dependency between an operating asset and a capability. |  Realized Functional Asset
Realized Functional Asset |
A kind of specialization between an implementing Functional Asset and its abstract Realized Functional Asset. Realization relationships are the foundation to establish the mapping between Functional Assets that belong to different Conceptualization Levels. References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Realization-Relationship |
 Satisfy (General) Satisfy (General) |
Generic satisfy relationship is a dependency between a requirement and a model element that fulfills the requirement. As with other dependencies, the arrow direction points from the satisfying (client) model element to the (supplier) requirement that is satisfied. | ||
 Satisfy (Policy) Satisfy (Policy) |
Satisfy relationship that is realization dependency between an operating asset and a policy |  Policy Conformance Policy Conformance |
A Policy Conformance is the conformity requirement that applies a Functional Asset. |
 UAFElement UAFElement |
Abstract super type for all of the UAF elements. It provides a way for all of the UAF elements to have a common set of properties. References: OMG - UAF - UAFElement |
 Asset Block
Asset Block |
An Asset Block is an Architecture Block used to describe the System Operating Framework - SOF of the enterprise and its systems. References: OMG - UAF - UAFElement OpenGroup - TOGAF - Architecture Building Blocks |
 Verify Verify |
A Verify relationship is a dependency between a requirement and a test case or other model element that can determine whether a system fulfills the requirement. As with other dependencies, the arrow direction points from the (client) element to the (supplier) requirement. |  Contraining Operational Policy
Contraining Operational Policy |
EXTERNAL REFERENCES
| Framework reference | SysFEAT Description |
|---|---|
 OMG - SACM : AssuranceCasePackage OMG - SACM : AssuranceCasePackage |
The assurance case concept doesn't exist in UAF. It is defined in OMG SCAM specification  Assurance Case
Assurance CaseAn Assurance Case is a claim that a particular enterprise asset or group of Functional Asset adequately mitigates certain identified Risk Types by means of appropriated Control Measures. An Assurance Case shall provide confidence that the concerned assets will function as intended in their environment of use. Privacy Processing Activity(ies), Data Lineages are examples of Assurance Cases . |
 OMG - SysML 1.X - Requirement OMG - SysML 1.X - Requirement |
A Requirement specifies a capability or condition that must (or should) be satisfied. A requirement may specify a function that a system must perform or a performance condition that a system must satisfy. Requirements are used to establish a contract between the customer (or other stakeholder) and those responsible for designing and implementing the system.  Requirement
RequirementA Requirement is a generic statement used in system engineering to constrain what a Business System Asset should or should not be. The Requirement concept is kept in SysFEAT to maintain compatibility with traditional system engineering methodologies. The preferred approach is to follow capability-based engineering, as promoted by modern enterprise & system architecture (see OMG - UAF - View - Strategic Views) and agile frameworks (see SAFe© - SAFe Requirements Model). |
 OMG - UAF - Asset OMG - UAF - Asset |
An abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be affected by Risk. Asset as applied to Security views is an abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be considered as a subject for security analysis An abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be affected by Risk. Asset as applied to Security views is an abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be considered as a subject for security analysis. An abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be affected by Risk. Asset as applied to Security views is an abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be considered as a subject for security analysis An abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be affected by Risk. Asset as applied to Security views is an abstract element that indicates the types of elements that can be considered as a subject for security analysis.  Functional Asset
Functional Asset Functional Assets encompasse all Asset Types used to describe why and how systems operate/function. This includes the Operating Eco-System where system operates to fulfill these purposes (Agent Types and their Behavior Types). Functional Assets include: 1. Blocks defining results of Behavior Types of the enterprise or its sub-systems, that benefit to it internal or external customers : Outcome Event, 2. Blocks used to describe information: Information Asset. 3. Blocks used to describe how the enterprise operates: Operating Asset Types (Agent Type, Behavior Type, Service Interface). |
 OMG - UAF - UAFElement OMG - UAF - UAFElement |
 Asset Block
Asset BlockAn Asset Block is an Architecture Block used to describe the System Operating Framework - SOF of the enterprise and its systems. Abstract super type for all of the UAF elements. It provides a way for all of the UAF elements to have a common set of properties. Abstract super type for all of the UAF elements. It provides a way for all of the UAF elements to have a common set of properties. |