CONCEPT DOMAIN - Data Governance Core
| Description | The Data Governance Core domain provides the core entities shared by all Data Governance sub-domains. Data Catalogs, along with their associated governance tools, form the central Management Systems that enable the execution of Data Governance objectives. |
|---|---|
| Dictionary |  Dictionary of SysFEAT concepts
Dictionary of SysFEAT concepts |
| Parent Domain | |
| Domain dependencies |  Deployed Facility Assets
Deployed Facility Assets  Information Assets
Information Assets  Operational Assurance
Operational Assurance  Policies
Policies |
DOMAIN CONCEPT GRAPH
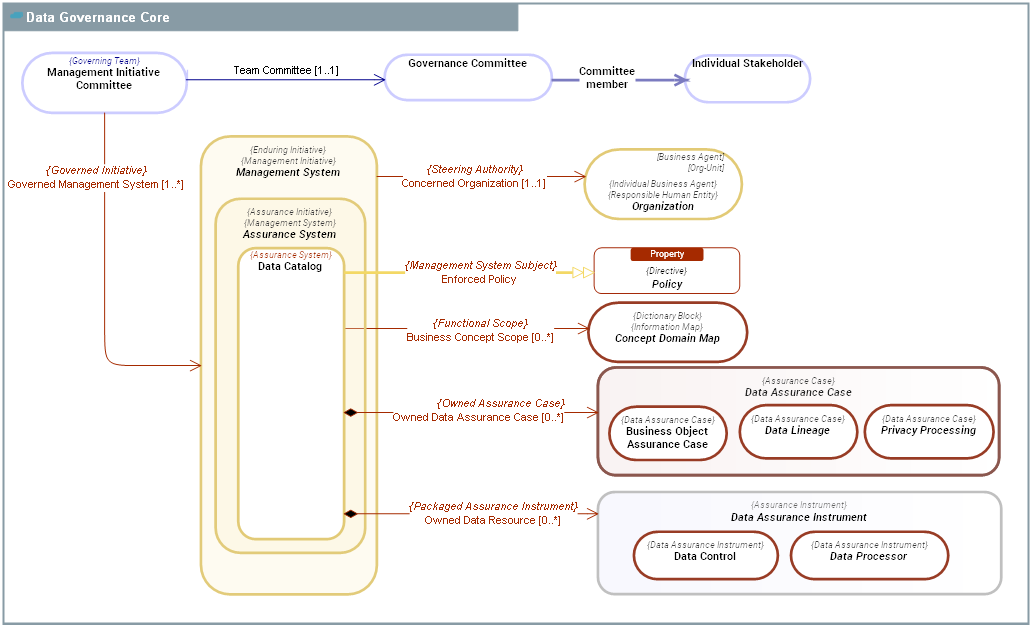
CONCEPT DESCRIPTIONS
ABSTRACT CONCRETE
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
 Assurance System
Assurance System |
An Assurance System is a Management System aimed at ensuring enterprise compliance, resilience, and risk mitigation against both internal and external Policys and threats. It encompasses processes, Directives and technologies that work in concert to validate enterprise adherence to policy requirements, industry standards, and internal policies while simultaneously bolstering the enterprise's ability to withstand and adapt to various challenges and disruptions. ensuring enterprise compliance and resilience against internal and external constraints: a. Regulation constraints: they defined what is allowed and not allowed by the law (See Regulation Article). b. Internal policies and rules constraints: they defined what is allowed and not allowed by the enterprise (see Business Policy). c. Operational constraints: they maintain operational capacities of the company (maintain ability to produce, maintain quality, ensure product development , ability to hire, to train, etc, see Business Rule). d. Architectural constraints: they guide design decisions and shape the overall structure of a system (see Architecture principle). |
 Data Assurance Case
Data Assurance Case |
A Data Assurance Case is a structured argument, supported by evidence, intended to justify that a data is acceptably assured relative to a concern (such as quality, safety, security or privacy) in the intended operating environment. The operating environment includes: 1. Policies related to the use of data in the organization (privacy policy, regulation policy, ...). 2. Data quality policies defined by the organization. 3. Risk to be mitigated in the use, consumption and sharing of data by the organization. 4. Control directives to be followed in the use, consumption and sharing of data by the organization.
|
 Data Assurance Instrument
Data Assurance Instrument |
A Data Assurance Instrument is a resource or course of actions used by an Data Catalog to achieve its objectives. For instance: Actions plans are course of actions aimed at solving Data breaches. Data Controls are mechanisms used to ensure data quality and data integrity Data Processors are used to processings involved in Data Lineages. |
 Data Lineage
Data Lineage |
A Data Lineage is about tracking the flow of information from source Information Assets to final Information Assets. It is necessary to guarantee the quality, usability and security of business data. For large organizations, it is also a key conformity legal requirement, for instance in BCBS 239 and Solvency II. Business Data Lineage is defined as a business data life cycle that describes the source of business data and where it moves over time. |
 Data Risk Type
Data Risk Type |
A Data Risk Type is a Risk Type that refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data during its entire lifecycle. |
 Information Asset
Information Asset |
An Information Asset represents anything that can be communicated or memorized by an Agent Type to produce and react to Outcome Events. An Information Asset is either an Information Entity or an Information Property.
The difference lies in their relationship to change and to time. Information Entity(ies) can change over time and have a lifeycle while Information Propertys are immutable characteristics. |
 Management System
Management System |
A Management System is a mezzo Enduring Initiative within an Enterprise, aimed at creating, maintaining, evaluating, evolving, and operating a collection of essential Functional Architecture Assets of the Enterprise. A Management System may transcend organisational boundaries and consequently requires an integrated team working under the direction of a Management Initiative Committee.
|
 Organization
Organization |
An Organization is a group of people who share a common purpose and establish a functional division of labor in pursuit of their common purpose. It is the relationships between its members in the pursuit of their common purpose that give unity and identity to an organization.
|
 Policy
Policy |
A Policy is a Directive that is not directly enforceable whose purpose is to govern, guide or constrain the structure and Behavior Type of Agent Types in the enterprise. Policies provide the basis for rules and govern Behavior Types carried out by Agent Types.
|
 Privacy Processing
Privacy Processing |
A Privacy Processing is a Data Assurance Case related to any operation or set of operations which is performed on personal data or on sets of personal data, whether or not by automated means, such as collection, recording, organisation, structuring, storage, adaptation or alteration, retrieval, consultation, use, disclosure by transmission, dissemination or otherwise making available, alignment or combination, restriction, erasure or destruction |
SERIALIZATION FORMAT
TEXTUAL SYNTAX RDF
 NIST - Assurance Case
NIST - Assurance Case