CONCEPT DOMAIN - Information Assets
| Description | Pattern Domain The Information Assets domain describes top level concepts used to describe information. |
|---|---|
| Dictionary |  SysFEAT System Operating Framework
SysFEAT System Operating Framework |
| Parent Domain |  Systemic Operating Ontology
Systemic Operating Ontology |
| Domain dependencies |  4D Composite Knowledge Graph
4D Composite Knowledge Graph  Architecture Assets
Architecture Assets  Information Packaging
Information Packaging  Reflexive Knowledge Graph
Reflexive Knowledge Graph  Risk & Threat
Risk & Threat  System Operating Framework - SOF
System Operating Framework - SOF |
DOMAIN CONCEPT GRAPH
CONCEPT DESCRIPTIONS
ABSTRACT CONCRETE
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
 Data Risk Type
Data Risk Type |
A Data Risk Type is a Risk Type that refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data during its entire lifecycle. |
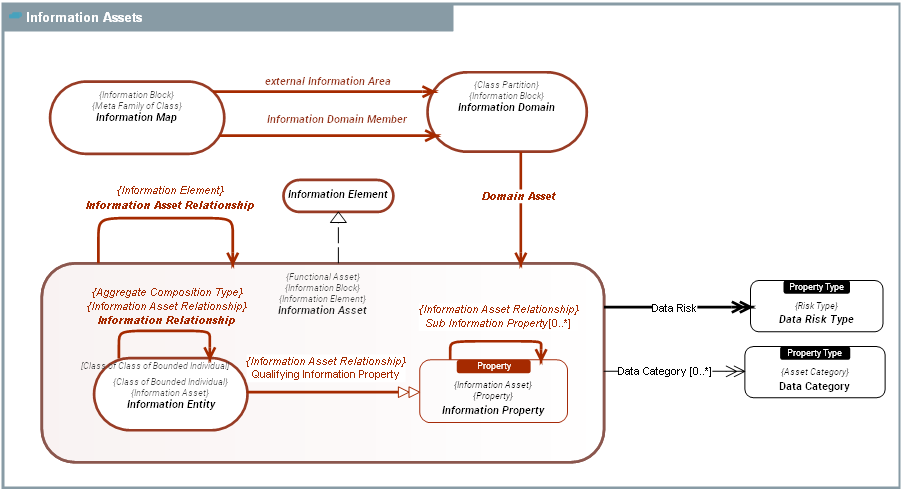
 Information Asset
Information Asset |
An Information Asset represents anything that can be communicated or memorized by an Agent Type to produce and react to Outcome Events. An Information Asset is either an Information Entity or an Information Property.
The difference lies in their relationship to change and to time. Information Entity(ies) can change over time and have a lifeycle while Information Propertys are immutable characteristics. |
 Information Block
Information Block |
An Information Block is an Asset Block involved in the description of information. Information Blocks range from Information Assets to Information Domains. They are packaged in Information Dictionary(ies) and managed in Data Catalogs. |
 Information Domain
Information Domain |
An Information Domain is a family of Information Entity(ies) which constitutes a unit a knowlege required by an Agent Type to operate during Behavior Type execution. |
 Information Entity
Information Entity |
An Information Entity is an Information Asset that is not fundamentally defined by its attributes, but rather by its continuity. An Information Entity evolves over time and has states. For instance a person is an Information Entity. Employe is a state of a person. An Information Entity has relationships to other Information Entitys and can have Information Propertys.
|
 Information Map
Information Map |
An Information Map is a Operating Property Map that is the top level grouping of Information Domains. Information Maps are used to provide navigationtop level entry points for Information Dictionary(ies) and to scope data management initiatives at the level of portfolio management ( Data Catalog), at the project level or at the Enterprise level (Enterprise Concept Map). |
 Information Property
Information Property |
An Information Property is an Information Asset that represents a characteristic (Class of Property) of an Information Entity. An Information Property is fundamentally defined by its value. It doesn't evolve over time and is thereby immutable. Examples: . Address. . Customer Name. . Amounts,
|
SERIALIZATION FORMAT
TEXTUAL SYNTAX RDF
 OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Passive-Structure-Elements
OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Passive-Structure-Elements Martin Fowler - Value Object
Martin Fowler - Value Object