CONCEPT DOMAIN - Logical Application Architecture
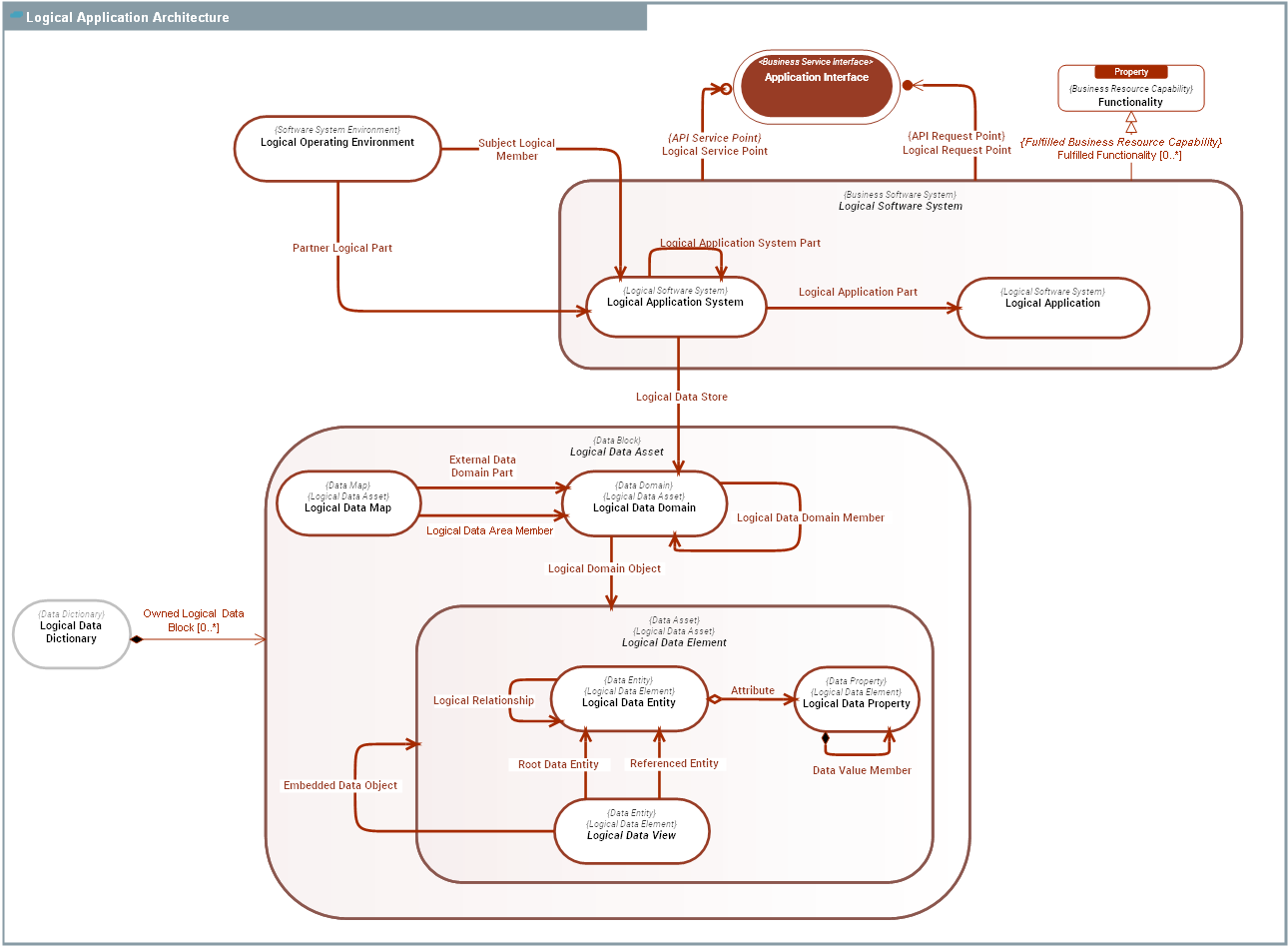
| Description | The Logical Application Architecture domain provides means of describing the logical structure and behavior of Business Software Systems of the enterprise. The aim of Logical Application Architecture is to describe an optimal optimal architecture of the enterprise IT systems. It is used to guide how key sub-systems and data domains are to be configured to meet IT systems missions and purposes. A Logical Application Architecture is concerned with how the IT Operating Model should look, not how it does look now. This includes: 1) Logical Application as the core building logical blocks for software components. 2) Logical Application System as consistent ssembly of Logical Applications. 3) Logical Data Domains of data entities. 4) Functionality(ies) fulfilled by logical systems. 5) Functional APIs exposed and used by applications: Application Interfaces. |
|---|---|
| Dictionary |  Dictionary of SysFEAT concepts
Dictionary of SysFEAT concepts |
| Parent Domain |  Software System ArcOps
Software System ArcOps |
| Domain dependencies |  EA Pattern - Data Domain
EA Pattern - Data Domain  SOF - Business Software Operating Model
SOF - Business Software Operating Model |
DOMAIN CONCEPT GRAPH
CONCEPT DESCRIPTIONS
ABSTRACT CONCRETE
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
 Logical Data Asset
Logical Data Asset |
A Logical Data Asset is a Data Asset used for the description of data consumed and produced by Logical Software Systems. Logical Data Assets are defined in Logical Data Dictionary(ies). |
 Logical Data Element
Logical Data Element |
A Logical Data Element represents the logical structure of any kind of data that can be memorized by a Business Software System. A Logical Data Element is either a Logical Data Entity or a Logical Data Property. Only Logical Data Entitys can have identity and can be referenced by Logical Relationships. Logical Data Propertys only handle raw data. |
 Logical Software System
Logical Software System |
A Logical Software System is logical specification of a Business Software System, which is independant from the Business Software System physical implementation. For instance, "Human Resource ERP System" is a Logical Application System, while "SAP HR System", "Sage HR System", "Kronos HR System" are Application Systems. |
SERIALIZATION FORMAT
TEXTUAL SYNTAX RDF
 EIP - messaging
EIP - messaging Martin Fowler - API Design
Martin Fowler - API Design
