IDENTITY - UAF - Information
| Description | Stakeholders: Data Modelers, Software Engineers, Systems Engineers Concerns: address the information perspective on operational, service, and resource architectures. Definition: allows analysis of an architecture’s information and data definition aspect, without consideration of implementation specific issues. Recommended Implementation: SysML Block Definition Diagram. |
|---|---|
| References | OMG - UAF - View - Information |
| Parent Mapping | UAF Mappings |
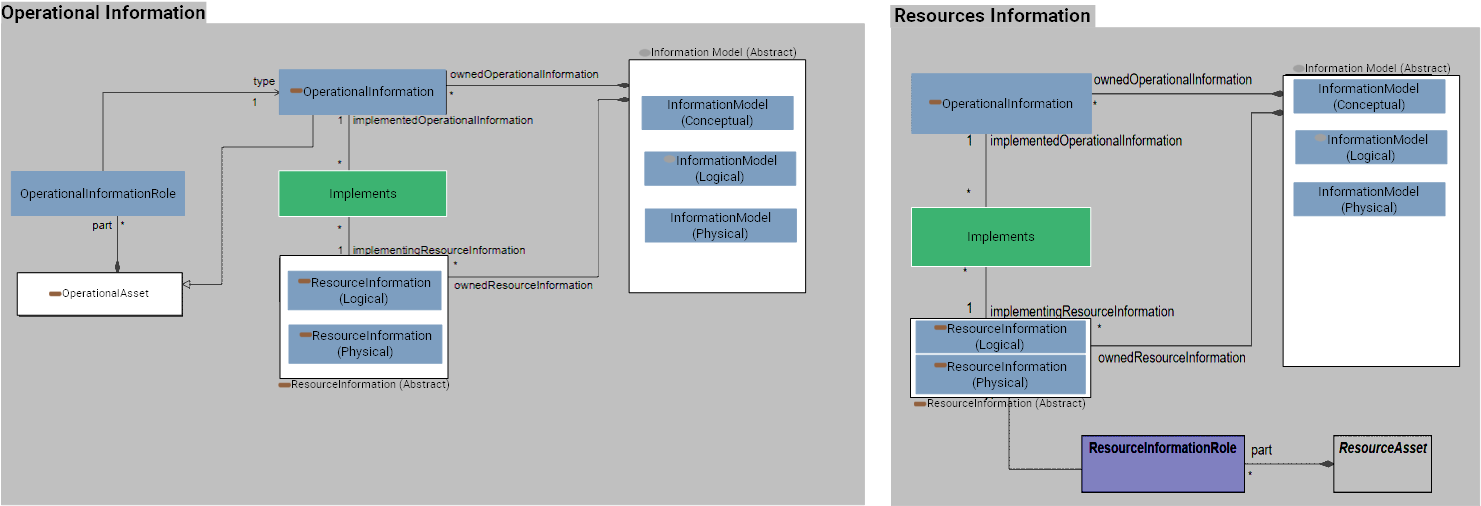
MAPPED ENTITIES
| Framework Concept | Framework Definition | SysFEAT Concept | SysFEAT Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
 Implements Implements |
A tuple that defines how an element in the upper layer of abstraction is implemented by a semantically equivalent element (for example tracing the Functions to the OperationalActivities) in the lower level of abstraction. References: OMG - UAF - Implements |
||
 Information Model (Abstract) Information Model (Abstract) |
A structural specification of data types, showing relationships between them. References: OMG - UAF - InformationModel |
 Information Dictionary
Information Dictionary |
An Information Dictionary is a Model Package of Information Blocks used to describe an information architecture. This includes: 1. Information Domain which groups Information Entitys by unit knowlege required by an Agent to operate during Behavior execution. 2. Information Entity which constitute resusable unit of information that can change over time. 3. Concept Property which constitue immutable characteristics of Information Entitys. Concrete implementations of Model Packages are Business Dictionary, Logical Data Dictionary, etc.
Information Model (Abstract) is not directly represented in SysFEAT. Rational: |
 InformationModel (Conceptual) InformationModel (Conceptual) |
Conceptual - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a conceptual InformationModel that defines the required high-level data concepts and their relationships. References: OMG - UAFML - InformationModelKind |
||
 InformationModel (Logical) InformationModel (Logical) |
Logical - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a logical data model that allows analysis of an architecture’s data definition aspect, without consideration of implementation specific or product specific issues. It details the conceptual data model/ References: OMG - UAFML - InformationModelKind |
 Logical Data Dictionary
Logical Data Dictionary |
Dictionary of Logical Data Entity. |
 InformationModel (Physical) InformationModel (Physical) |
Physical - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a physical data model that is an implementable specification of a data structure. A physical data model realizes a logical data model, taking into account implementation restrictions and performance issues while still enforcing the constraints, relationships and typing of the logical data model. References: OMG - UAFML - InformationModelKind |
||
 OperationalAsset OperationalAsset |
An abstract element used to group the elements of OperationalAgent and OperationalInformation allowing them to own OperationalInformationRoles. References: OMG - UAF - OperationalAsset |
 Conceptual Operating Asset
Conceptual Operating Asset |
A Conceptual Operating Asset is an Operating Asset Type used to describe the Conceptual Operating Model of the enterprise. It includes Value Streams, Operating Domains and Business Functions and the way they contribute to the delivery of Business Outcome Events. References: OMG - UAF - OperationalAsset |
 OperationalInformation OperationalInformation |
An item of information that flows between OperationalPerformers and is produced and consumed by the OperationalActivities that the OperationalPerformers are capable to perform (see IsCapableToPerform). References: OMG - UAF - OperationalInformation |
 Conceptual Entity Asset
Conceptual Entity Asset |
A Conceptual Entity Asset is the representation of any type of tangible or intanglible resource, or its respective state, that is critical for comprehending an enterprise, including its data, resources, and activities. Similar to any Information Asset, a Conceptual Entity Asset can be classified into three categories: 1) Conceptual Entitys denote entities that can change over time. 2) Event Concepts embody the temporal boundaries associated with Conceptual Entitys. 3) Concept Propertys represent immutable characteristics of Conceptual Entitys. References: OMG - BACM - Business Object OMG - UAF - OperationalInformation Russell Ackoff - Choice & Communication - Concept |
 OperationalInformationRole OperationalInformationRole |
A usage of OperationalInformation that exists in the context of an OperationalAsset. It also allows the representation of the whole-part aggregation of OperationalInformation. |  Information Store
Information Store |
An Information Store is a storage of Information Assets necessary for an Agent Type to carry out its activities. The scope of the necessary Information Assets is given by the Information Domain associated with the Information Store. |
 ResourceInformation (Abstract) ResourceInformation (Abstract) |
A formalized representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. References: OMG - UAF - ResourceInformation |
 Data Asset
Data Asset |
A Data Asset represents the abstract structure of any kind of data that can be processed and memorized by a Business Software System. A Data Asset is either a Data Entity or a Data Property. Only Data Entitys can have identity and states. Data Propertys only handle raw data. Data Assets are managed in Data Catalogs. References: NIST - Data Asset UCF Glossary - Data UCF Glossary - Data Element |
 ResourceInformation (Logical) ResourceInformation (Logical) |
A formalized logical representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. References: OMG - UAF - ResourceInformation |
 Logical Data Element
Logical Data Element |
A Logical Data Element represents the logical structure of any kind of data that can be memorized by a Business Software System. A Logical Data Element is either a Logical Data Entity or a Logical Data Property. Only Logical Data Entitys can have identity and can be referenced by Logical Relationships. Logical Data Propertys only handle raw data. |
 ResourceInformation (Physical) ResourceInformation (Physical) |
A formalized physical representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. References: OMG - UAF - ResourceInformation |
 Physical Data Asset
Physical Data Asset |
A Physical Data Asset represents the physical structure of any kind of data that can be memorized by a Business Software System. A Physical Data Asset is either a Physical Data Entity or a Physical Data Property. Only Physical Data Entitys can have an identity can by be referenced by Physical Relationship. Physical Data Property only handle raw data. |
EXTERNAL REFERENCES
| Framework reference | SysFEAT Description |
|---|---|
 OMG - UAF - Implements OMG - UAF - Implements |
A tuple that defines how an element in the upper layer of abstraction is implemented by a semantically equivalent element (for example tracing the Functions to the OperationalActivities) in the lower level of abstraction. A tuple that defines how an element in the upper layer of abstraction is implemented by a semantically equivalent element (for example tracing the Functions to the OperationalActivities) in the lower level of abstraction. A tuple that defines how an element in the upper layer of abstraction is implemented by a semantically equivalent element (for example tracing the Functions to the OperationalActivities) in the lower level of abstraction. A tuple that defines how an element in the upper layer of abstraction is implemented by a semantically equivalent element (for example tracing the Functions to the OperationalActivities) in the lower level of abstraction. A tuple that defines how an element in the upper layer of abstraction is implemented by a semantically equivalent element (for example tracing the Functions to the OperationalActivities) in the lower level of abstraction. A tuple that defines how an element in the upper layer of abstraction is implemented by a semantically equivalent element (for example tracing the Functions to the OperationalActivities) in the lower level of abstraction. |
 OMG - UAF - InformationModel OMG - UAF - InformationModel |
A structural specification of data types, showing relationships between them. |
 OMG - UAF - OperationalAsset OMG - UAF - OperationalAsset |
 Conceptual Operating Asset
Conceptual Operating AssetA Conceptual Operating Asset is an Operating Asset Type used to describe the Conceptual Operating Model of the enterprise. It includes Value Streams, Operating Domains and Business Functions and the way they contribute to the delivery of Business Outcome Events. An abstract element used to group the elements of OperationalAgent and OperationalInformation allowing them to own OperationalInformationRoles. An abstract element used to group the elements of OperationalAgent and OperationalInformation allowing them to own OperationalInformationRoles. |
 OMG - UAF - OperationalInformation OMG - UAF - OperationalInformation |
 Concept
ConceptA Concept is the representation of any tangible or intanglible entity that is of interest to understand the enterprise, its data, resources and activities. A Concept is defined through its essential characteristics which can be: 1) A Concept Property that represents some an immutable factual characteristic such as "name", "amount". 2) A Concept Relationship that represents relationships to other Concepts.  Concept Property v
Concept Property vA Concept Property v is an immutable factual characteristic of a Conceptual Entity. Example: names, amounts, etc.  Conceptual Entity Asset
Conceptual Entity AssetA Conceptual Entity Asset is the representation of any type of tangible or intanglible resource, or its respective state, that is critical for comprehending an enterprise, including its data, resources, and activities. Similar to any Information Asset, a Conceptual Entity Asset can be classified into three categories: 1) Conceptual Entitys denote entities that can change over time. 2) Event Concepts embody the temporal boundaries associated with Conceptual Entitys. 3) Concept Propertys represent immutable characteristics of Conceptual Entitys. An item of information that flows between OperationalPerformers and is produced and consumed by the OperationalActivities that the OperationalPerformers are capable to perform (see IsCapableToPerform). An item of information that flows between OperationalPerformers and is produced and consumed by the OperationalActivities that the OperationalPerformers are capable to perform (see IsCapableToPerform). |
 OMG - UAF - ResourceInformation OMG - UAF - ResourceInformation |
 Logical Data Entity
Logical Data EntityA Logical Data Entity is a logical structure of a Data Entity. As any Data Entity, it has an independent existence and can be uniquely identified. A Logical Data Entity is characterized by Logical Relationships it has with other Logical Data Entity(ies) and by its Attributes. A formalized representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. A formalized representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. A formalized representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. A formalized representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. A formalized logical representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. A formalized physical representation of information that is managed by or exchanged between systems. |
 OMG - UAFML - InformationModelKind OMG - UAFML - InformationModelKind |
Logical - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a logical data model that allows analysis of an architecture’s data definition aspect, without consideration of implementation specific or product specific issues. It details the conceptual data model. Conceptual - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a conceptual InformationModel that defines the required high-level data concepts and their relationships. Conceptual - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a conceptual InformationModel that defines the required high-level data concepts and their relationships. Conceptual - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a conceptual InformationModel that defines the required high-level data concepts and their relationships. Logical - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a logical data model that allows analysis of an architecture’s data definition aspect, without consideration of implementation specific or product specific issues. It details the conceptual data model/ Physical - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a physical data model that is an implementable specification of a data structure. A physical data model realizes a logical data model, taking into account implementation restrictions and performance issues while still enforcing the constraints, relationships and typing of the logical data model. Physical - Indicates that the InformationModel associated with the InformationModelKind is a physical data model that is an implementable specification of a data structure. A physical data model realizes a logical data model, taking into account implementation restrictions and performance issues while still enforcing the constraints, relationships and typing of the logical data model. |