IDENTITY - ArchiMate - Application Layer
| Description | The Application Layer elements are typically used to model the Application Architecture that describes the structure, behavior, and interaction of the applications of the enterprise. |
|---|---|
| References | OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Layer - Application Layer |
| Parent Mapping | ArchiMate Mapping |
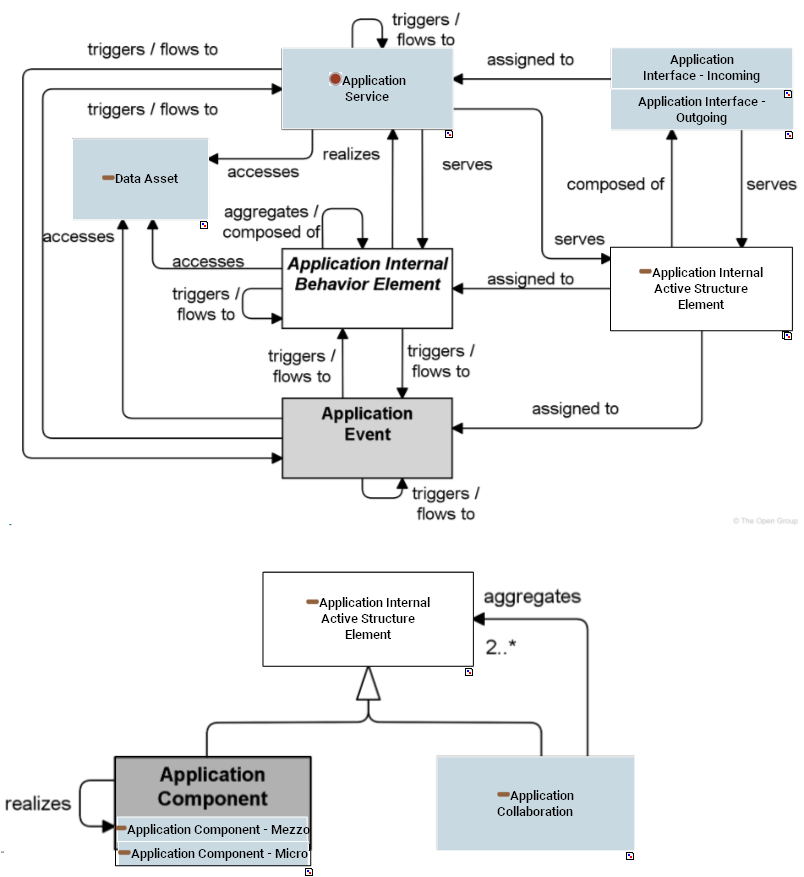
MAPPED ENTITIES
| Framework Concept | Framework Definition | SysFEAT Concept | SysFEAT Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
 Application Collaboration Application Collaboration |
References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application-Collaboration |
 Application System
Application System |
An Application System is a Business Software System which is an assembly of multiple Applications or other Application Systems that, together, fulfill a set of Macro Functionality(ies) delivered to Business Operations. Application Systems are used in the context of IT Strategic planning to define and evolve other time the hight level structure of the enterprise IT Architecture. Application System is a Macro enterprise asset that sit at the top of Business Software System decomposition hierarchy. Example: "HR System" is an Application System whereas "Payroll" is an Application that is part of the "HR system". References: C4 Model - Supplementary diagrams - System Landscape diagram OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application-Collaboration |
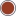
 Application Component - Mezzo Application Component - Mezzo |
References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Component |
 Application
Application |
An Application is a Business Software System that provides a set of Functionality(ies) that End Users see as a single unit. Essentially Applications are architectural constructions resulting from the combinaison of the following four criteria: 1) A group of Functionality that End Users see as a single unit. 2) A managed asset (Managed Application) associated with a budget line in the context of an Application Portfolio. 3) A body of code that is seen by developers as a single unit. 4) A group of deployable software units (Deployable Application Packages) that must be installed together on one or multiple execution nodes (Computing System). Application is a Mezzo enterprise asset that sits between Application System and Application Component in the decomposition of Business Software Systems. Example: " Payroll" is an Application that is part an " HR System" which is an Application System. The "Payroll" Application includes, among other things, the "Salary and Wage Calculation" Application Component. References: C4 Model - Software System Martin Fowler - Application Boundary Microsoft - Architecture Design - Architecture Styles OMG - UAF - Software OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Component OpenGroup - TOGAF - Definition - Application Component OpenGroup - TOGAF - Enterprise Metamodel - Physical Application Component |
 Application Component - Micro Application Component - Micro |
References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Component |
 MicroService
MicroService |
A MicroService is a small autonomous unit of software, emphasizing self-management and lightweightness as the means to improve software agility, scalability, and autonomy. 1) MicroServices are automous or assembled and orchestrated as components of Applications. 2) MicroServices can be directly deployed to Computing Systems. MicroServices are both a logical unit of software and a Deployable Package. 3) MicroServices owns their own data store and dot not have any shared stores with other components. MicroService is a Micro enterprise asset that sits at the lower level of Business Software System decomposition. References: C4 Model - Level 2 - Container Diagram C4 Model - Level 3 - Component Diagram Martin Fowler - Micro-Service Microsoft - Architecture Design - Microservice architecture style OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Component |
 Application Interface - Incoming Application Interface - Incoming |
 API Service Point
API Service Point |
References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Interface |
|
 Application Interface - Outgoing Application Interface - Outgoing |
 API Request Point
API Request Point |
References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Interface |
|
 Application Internal Active Structure Element Application Internal Active Structure Element |
References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Internal Active Structure Element |
 Business Software System
Business Software System |
A Business Software System is a Business System used by Business Operations, that represents all granularities of software - ranging from MicroServices to enterprise wide Application Systems - used by Business Operations. All Business Software Systems share the following characteristics: 1) They provide Functionalitys. 2) They expose APIs (Application Interfaces) through which they deliver Information Outcome Events. 3) They handle datastores defined by Physical Data Domains. 4) They perform and participate to System Processes. References: OMG - UAF - Software OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Internal Active Structure Element OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Layer - Application Layer UCF Glossary - Software Asset |
 Application Internal Active Structure Element Application Internal Active Structure Element |
References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Internal Active Structure Element |
 Business Software System
Business Software System |
A Business Software System is a Business System used by Business Operations, that represents all granularities of software - ranging from MicroServices to enterprise wide Application Systems - used by Business Operations. All Business Software Systems share the following characteristics: 1) They provide Functionalitys. 2) They expose APIs (Application Interfaces) through which they deliver Information Outcome Events. 3) They handle datastores defined by Physical Data Domains. 4) They perform and participate to System Processes. References: OMG - UAF - Software OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Internal Active Structure Element OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Layer - Application Layer UCF Glossary - Software Asset |
 Application Service Application Service |
References: OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Service |
 Application Interface
Application Interface |
An Application Interface is a Business Service Interface that occurs between Business Software Systems. The interface is described by messages exchanged between endpoints (provider, consumer..). References: EIP - messaging Martin Fowler - API Design Martin Fowler - Richardson Maturity Model Microsoft - Architecture Design - RESTful web API design OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Service OpenGroup - IT4IT - Defining Service Reference Architecture |
 Data Asset Data Asset |
 Data Asset
Data Asset |
A Data Asset represents the abstract structure of any kind of data that can be processed and memorized by a Business Software System. A Data Asset is either a Data Entity or a Data Property. Only Data Entitys can have identity and states. Data Propertys only handle raw data. Data Assets are managed in Data Catalogs. References: NIST - Data Asset UCF Glossary - Data UCF Glossary - Data Element |
EXTERNAL REFERENCES
| Framework reference | SysFEAT Description |
|---|---|
 OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Component OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Component |
 Application
ApplicationAn Application is a Business Software System that provides a set of Functionality(ies) that End Users see as a single unit. Essentially Applications are architectural constructions resulting from the combinaison of the following four criteria: 1) A group of Functionality that End Users see as a single unit. 2) A managed asset (Managed Application) associated with a budget line in the context of an Application Portfolio. 3) A body of code that is seen by developers as a single unit. 4) A group of deployable software units (Deployable Application Packages) that must be installed together on one or multiple execution nodes (Computing System). Application is a Mezzo enterprise asset that sits between Application System and Application Component in the decomposition of Business Software Systems. Example: " Payroll" is an Application that is part an " HR System" which is an Application System. The "Payroll" Application includes, among other things, the "Salary and Wage Calculation" Application Component.  Application Component
Application ComponentAn Application Component is a functionnal unit of software (java class, COBOL Program, Batch) that is a consistent, indivisible unit of processing of an Application producing and consuming its Information Outcome Events though APIs (Application Interface). a) Application Components are assembled and orchestrated in Applications. b) Application Components cannot be directly deployed to Computing Systems: they need to be organized in Deployable Application Packages. Application Component is a Micro enterprise asset that sits at the lowest level of Business Software System decomposition. Example: the "Salary and Wage Calculation" component is an Application Component that is part of the "Payroll" Application.  MicroService
MicroServiceA MicroService is a small autonomous unit of software, emphasizing self-management and lightweightness as the means to improve software agility, scalability, and autonomy. 1) MicroServices are automous or assembled and orchestrated as components of Applications. 2) MicroServices can be directly deployed to Computing Systems. MicroServices are both a logical unit of software and a Deployable Package. 3) MicroServices owns their own data store and dot not have any shared stores with other components. MicroService is a Micro enterprise asset that sits at the lower level of Business Software System decomposition. |
 OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Internal Active Structure Element OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Internal Active Structure Element |
 Business Software System
Business Software SystemA Business Software System is a Business System used by Business Operations, that represents all granularities of software - ranging from MicroServices to enterprise wide Application Systems - used by Business Operations. All Business Software Systems share the following characteristics: 1) They provide Functionalitys. 2) They expose APIs (Application Interfaces) through which they deliver Information Outcome Events. 3) They handle datastores defined by Physical Data Domains. 4) They perform and participate to System Processes. |
 OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Service OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application Service |
 Application Interface
Application InterfaceAn Application Interface is a Business Service Interface that occurs between Business Software Systems. The interface is described by messages exchanged between endpoints (provider, consumer..). |
 OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application-Collaboration OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Application-Collaboration |
 Application System
Application SystemAn Application System is a Business Software System which is an assembly of multiple Applications or other Application Systems that, together, fulfill a set of Macro Functionality(ies) delivered to Business Operations. Application Systems are used in the context of IT Strategic planning to define and evolve other time the hight level structure of the enterprise IT Architecture. Application System is a Macro enterprise asset that sit at the top of Business Software System decomposition hierarchy. Example: "HR System" is an Application System whereas "Payroll" is an Application that is part of the "HR system". |