CONCEPT DOMAIN - Reflexive Knowledge Graph
| Description | The Reflexive Knowledge Graph domain defines the top level constructs of Entitys, Relationships, their multi-level classification and mereological relationships. It forms the second layer of SysFEAT's graph architecture. In this domain, Relationships are refied as first class Elements, allowing them to be further described and qualified. Multi-level classification is implemented by PowerTyping, which enables open and flexible meta-modeling capabilities, This includes support for reflexive meta-modeling, for example allowing Meta-Class to be an instance of itself. Powertyping also applies to relationships, including the Holonymy relationship. This design grounds the Reflexive Knowledge Graph in non-well-founded set theory, ensuring consistency in circular and self-referential structures (see associated external references). The 4D Composite Knowledge Graph provides additional structuring of Entitys and Relationships by implementing the Compositionality pattern which establishes the concepts of dynamic locality and connections. |
|---|---|
| External references |
 Matthew West - Ontology meets Business - Non well founded sets Matthew West - Ontology meets Business - Non well founded sets
 Multi-level conceptual modeling: Theory, language and application Multi-level conceptual modeling: Theory, language and application
 OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Top Level Language Structure OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Top Level Language Structure
 Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Non-wellfounded set theory Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Non-wellfounded set theory
 WordNet - Abstraction WordNet - Abstraction
 Wordnet - Semantics Wordnet - Semantics
 WordNet - Typology WordNet - Typology
|
| Dictionary |  SysFEAT Upper Ontology
SysFEAT Upper Ontology |
| Parent Domain |  Upper Ontology
Upper Ontology |
| Domain dependencies |  Elementary Graph
Elementary Graph |
DOMAIN CONCEPT GRAPH
CONCEPT DESCRIPTIONS
ABSTRACT CONCRETE
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
 Abstract Entity
Abstract Entity |
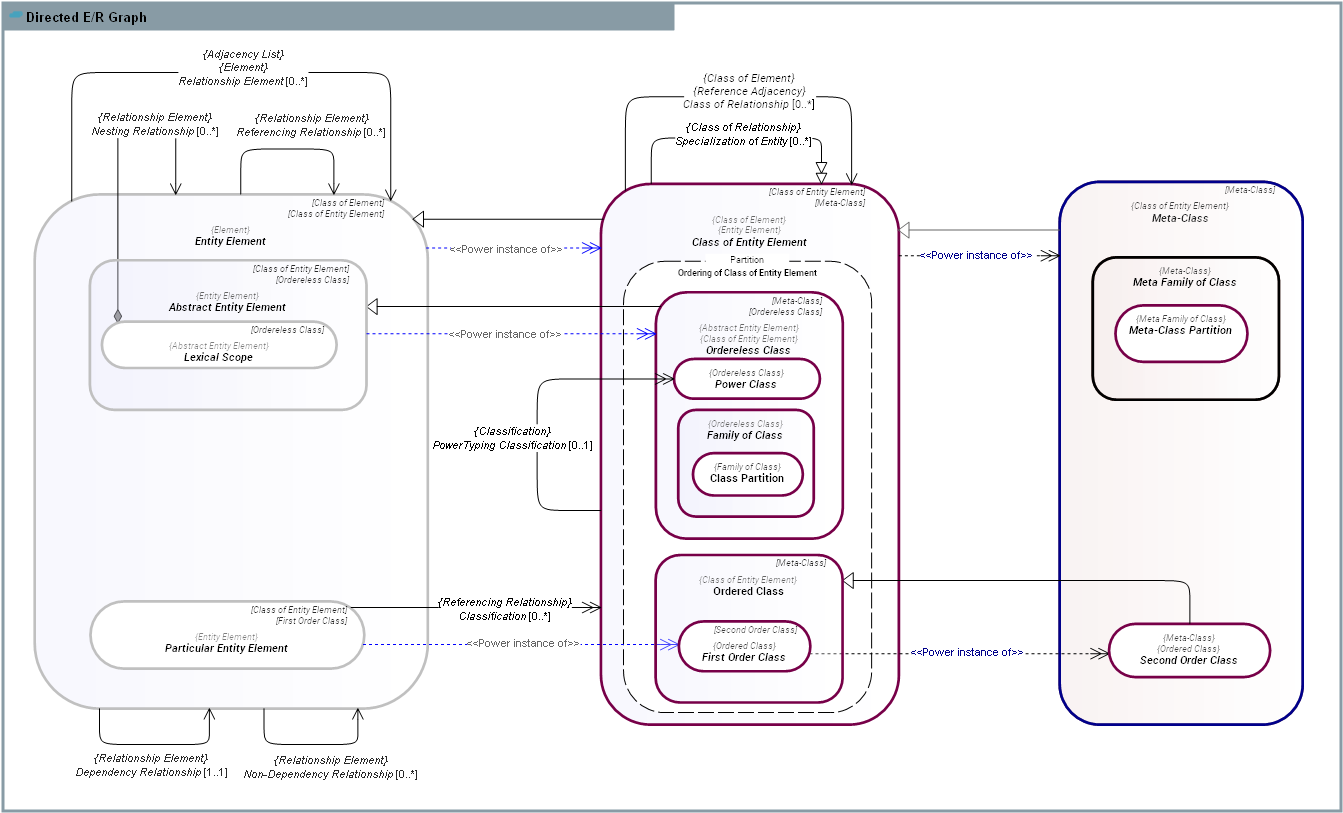
Abstract Entity is a class of Entitys that cannot have direct instances and represents aspects of entities. It is the power instance of Orderless Class, which means that its sub-types can belong to any Ordered Class. Example: 1) Aspects of Entitys, such as Lexical Scope. 2) Propertys of Individuals. |
 Class of Entity
Class of Entity |
A Class of Entity is a Class of Element that classifies Entitys. Being a subtype of Entity, it is also an instance of itself. Note: 1) SysFEAT is a higher-order ontology, so Class of Entity may have members that are also Class of Entity (Class of Classes). 2) SysFEAT is also a non-well-founded allows for self-referencing Class of Entity.
|
 Class Partition
Class Partition |
|
 Concrete Entity
Concrete Entity |
Concrete Entity is a class whose instances are classifed by an Ordered Class: it is the power instance of Ordered Class. Examples: |
 Entity
Entity |
An Entity is a distinct, identifiable Element that has a proper existence (living or non living). It is accessible by some referencing mechanism and can establish elementary relationships (Relationship) to other Entitys. The Entity class is the powerinstance of Class of Entity: all subtypes of Entity are instances of Class of Entity.
|
 Family of Class
Family of Class |
|
 First Order Class
First Order Class |
First Order Class is the Meta-Class of all subclasses of Particular Entity. Each instance of First Order Class is a Class of Entity, each of whose instances is necessarily a Particular Entity.
|
 Lexical Scope
Lexical Scope |
A Lexical Scope is a kind of Abstract Entity that defines the existence, visibility, and accessibility of the entities nested within it through a Nesting Relationship. Nested Entitys have no independent identity or validity outside the lexical or structural scope in which they are defined - they exist only within and for the duration of their parent construct. Every Entity belongs to exactly one Lexical Scope. A Lexical Scope carries no intrinsic semantic meaning; it serves purely as a syntactic mechanism for establishing hierarchical containment. Examples: 1) Composite structures (Aggregate Block) nesting their internal constituents (Aggregate Member). 2) Social structures nesting their roles and functions. 3) Computer functions nesting their local variables or inner functions 4) Packages nesting their Building Blocks.
|
 Meta Family of Class
Meta Family of Class |
A Meta Family of Class is a Class of Classes of Element (its members are themselves Class of Elements), typically used to group or organize collections of Class of Elements that share some structural, relational, or definitional property. In contrast to families of sets, which are sets of sets, a family of classes operates at a higher ontological level-its elements may represent universes, types, or conceptual groupings rather than individual sets.
|
 Meta-Class
Meta-Class |
Meta-Class (also called Class of Classes of Entity) is the Class of Entity of all Class of Entitys each of whose instances is necessarily a Class of Entity. In other word, Meta-Class is the powertype of Class of Entity: all sub-classes of Class of Entitys are instances of Meta-Class. Since Meta-Class is itself a sub-type of Class of Entity, Meta-Class is an instance of itself.
|
 Ordered Class
Ordered Class |
Ordered Class is the Meta-Class (subtype of Class of Entity and instance of Meta-Class) of all power-type based Class of Entitys that follow a strict ordering of metalevels. |
 Orderless Class
Orderless Class |
An Orderless Class is a Class of Entity which instances can belong to different meta-modeling order. This includes Class of Entitys that are instances of themselves, such as . |
 Particular Entity
Particular Entity |
A Particular Entity is a Concrete Entity that is not itself a class (Class of Entity): it cannot have instances. The " Particular Entity" class is the powerinstance of First Order Class. Particular Entitys are the most common type of entities. The word "Individual" is sometimes used to designate particulars. In SysFEAT, the term Individual is reserved for particulars that have a spatio-temporal extent. Examples: . The set of numbers {1,2,3,4}. . The mathematical constant π (pi). . The English word "Tree" (as a specific string of characters in a specific language). . The Eiffel tower (31st March 1889 - ...). . Mount Vesuvius eruption (Aug. 24-25, A.D. 79). |
 Second Order Class
Second Order Class |
Second Order Class is the Meta-Class of all subclasses of First Order Class. Each instance of Second Order Class is a class, each of whose instances is a First Order Class. First Order Class is an instance of Second Order Class since, by definition, all of its instances are First Order Classes. Examples: 1) Car-Brand (with instances such as VolkswagenCar and HondaCar), 2) AnimalSpecies (with instancessuch as GreyWolf and Dodo), Occupation, and USArmyRank.
|
SERIALIZATION FORMAT
TEXTUAL SYNTAX RDF