IDENTITY - BMM Mapping
| Description | Mapping of the OMG BMM metamodel with SysFEAT Concepts. |
|---|---|
| References | OMG - BMM - Overview |
| Corresponding SysFEAT Domain | Enterprise Strategy & Roadmapping |
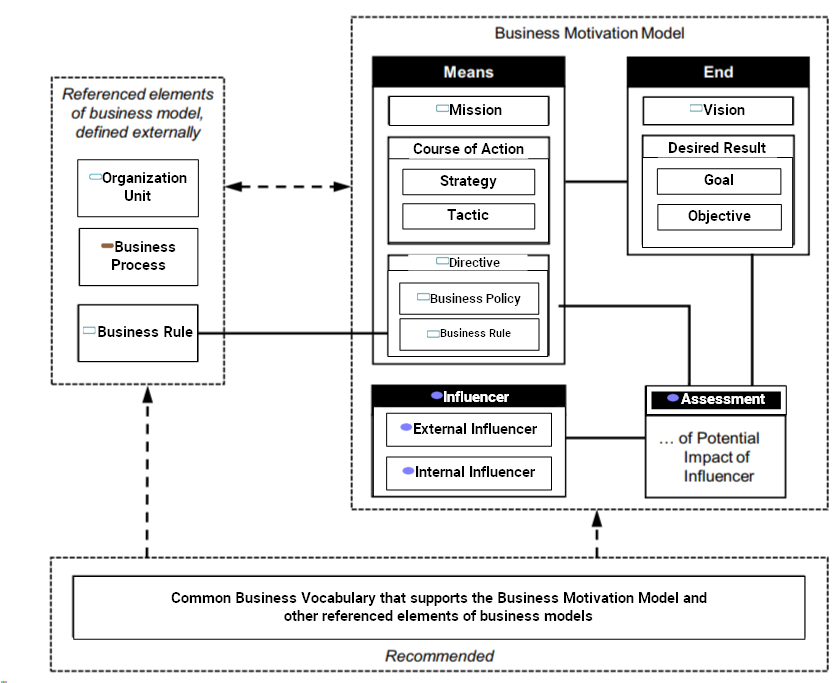
MAPPED ENTITIES
| Framework Concept | Framework Definition | SysFEAT Concept | SysFEAT Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
 Assessment Assessment |
An Assessment is a judgment of some Influencer that affects the organization’s ability to employ its Means or achieve its Ends. In other words, an Assessment expresses a logical connection (i.e., fact type) between Influencers and the Ends and/ or Means of the business plans. In this way, an Assessment indicates which Influencers are relevant to which Ends and/or Means. References: OMG - BMM - Assessment |
 Driver Assessment
Driver Assessment |
A Driver Assessment is a kind of Assessment which is motivated by a Stakeholder Driver. References: OMG - UAF - Challenge |
 Business Policy Business Policy |
A Business Policy is a Directive that is not directly enforceable8 whose purpose is to govern or guide the enterprise. Business Policies provide the basis for Business Rules. Business Policies also govern Business Processes References: OMG - BMM - Business Policy |
 Business Policy
Business Policy |
A Business Policy is a Policy that is not directly enforceable whose purpose is to govern or guide the enterprise. References: OMG - BMM - Business Policy |
 Business Process Business Process |
Business Processes realize Courses of Action. They provide processing steps, sequences (including cycles, branches, and synchronization), structure (decomposition and reuse), interactions, and connection to events that trigger the processes. Courses of Action are governed by Business Policies; Business Processes are also governed by Business Policies. References: OMG - BMM - Business Process |
 Business Process
Business Process |
A Business Process is a set of Business-Process Steps performed by Org-Unit Types and/or by automated systems (Business Systems) to produce a Business Outcome Event. It is depicted as a series of Business-Process Steps, controlled by Business Events and conditions. Business-Process Steps are carried out by the involvment of Org-Unit Types and system resources (often Applications) as participants in the process (Participant Business Agents). During its course of action, a Business Process consumes or produces Business Objects. 1) It may memorize or access Business Objects from its Process Store. 2) It may receive Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Consumption. 3) It may signal the production of Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Production. The course of actions of a Business Process is constrained by the application of rules ( Business Rule Enforcement) that define how to react to what is allowed and not allowed to do, References: ISO 9000 - 3.4.1 - Process Lean.org - Value Stream Lean.org - Value Stream Mapping OMG - BMM - Business Process OMG - BPMN - Process OMG - UAF - Function OpenGroup - OAA - Process OpenGroup - TOGAF - Enterprise Metamodel Overview OpenGroup - TOGAF 9 - Definition - Process |
 Business Rule Business Rule |
Business Rules provide specific, practicable guidance to implement Business Policies. Some Business Rules could be automated in software; some are practicable only by people. References: OMG - BMM - Business Rule |
 Business Rule
Business Rule |
A Business Rule is a rule that is under business jurisdiction. A rule’s being under "business jurisdiction" means that it is under the jurisdiction of the community that it governs or guides - that the community can opt to change or discard the rule. Laws of physics may be relevant to an Enterprise; legislation and regulations may be imposed on it; external standards. These things are not Business Rules from the company’s perspective, since it does not have the authority to change them. The company will decide how to react to laws and regulations, and will create Business Rules to ensure compliance with them. Similarly, it will create Business Rules to ensure that standards or best practices are implemented as intended. |
 Common Business Vocabulary that supports the Business Motivation Model and other referenced elements of business models Common Business Vocabulary that supports the Business Motivation Model and other referenced elements of business models |
References: OMG - BMM - Common Vocabulary |
||
 Course of Action Course of Action |
A Course of Action is an approach or plan for configuring some aspect of the enterprise involving things, processes, locations, people, timing, or motivation undertaken to achieve Desired Results. In other words, a Course of Action channels efforts towards Desired Results. To help ensure success in this regard, Courses of Action are governed by Directives. References: OMG - BMM - Course of Action |
||
 Desired Result Desired Result |
A Desired Result is an End that is a state or target that the enterprise intends to maintain or sustain. A Desired Result is supported by Courses of Action. |
||
 Directive Directive |
As the name suggests, Directives indicate how the Courses of Action should, or should not, be carried out (in other words, they govern Courses of Action). Specifically, a Directive defines or constrains or liberates some aspect of an enterprise. It is intended to assert business structure or to control or influence the behavior of the business, and is stated in declarative form. References: OMG - BMM - Directive |
 Directive
Directive |
A Directive is an authoritative declaration that indicates how Agents and their Behaviors should be (or should not be) in the enterprise. Specifically, a Directive defines, constrains or liberates some aspects of an Agent and its Behaviors. As such, Directives shall be considered as constraning Asset Propertys. Directives are intended to assert agent structures or to control or influence their Behaviors. Directives are stated in declarative form. References: OMG - BMM - Directive OMG - SBVR - Element of Guidance OMG - UAF - Rule OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Constraint UCF Glossary - Directive |
 External Influencer External Influencer |
An influencer that is outside the enterprise’s organizational boundaries. References: OMG - BMM - External Influencer |
 Exogenous Driver
Exogenous Driver |
An Exogenous Driver is an external Driver whose source of change is outside the enterprise’s organizational boundaries and that can impact its employment of Means or achievement of Ends. References: OMG - BMM - External Influencer |
 Goal Goal |
A Goal is a statement about a state or condition of the enterprise to be brought about or sustained through appropriate Means. A Goal amplifies a Vision; that is, it indicates what must be satisfied on a continuing basis to effectively attain the Vision. References: OMG - BMM - Goal |
 Enterprise Goal
Enterprise Goal |
An Enterprise Goal is an ideal target Value Proposition that tends to be longer term, and is defined qualitatively rather than quantitatively. It should be sufficiently narrow-focused so that Objectives can be defined for it. References: OMG - BMM - Goal OMG - UAF - EnterpriseGoal Russell Ackoff - System of Concepts - Objective UCF Glossary - Enterprise Objective |
 Influencer Influencer |
An Influencer is something that can cause changes that affect the enterprise in its employment of its Means or achievement of its Ends. Alternatively, it might confirm that there are no changes where changes might have been expected. References: OMG - BMM - Influencer |
 Driver
Driver |
A Driver is a factor which can have a significant impact on the activities, and goals of an Enterprise or a Management System. References: ISO 42010 - Concern OMG - BMM - Influencer OMG - UAF - Driver OpenGroup - TOGAF - Definitions - Concern |
 Internal Influencer Internal Influencer |
An influencer from within the enterprise. References: OMG - BMM - Internal Influencer |
 Endogenous Driver
Endogenous Driver |
Endogenous Drivers are those which subject of concern are within an enterprise that can impact its employment of Means or achievement of Ends. References: OMG - BMM - Internal Influencer |
 Mission Mission |
A Mission indicates the ongoing operational activity of the enterprise. The Mission describes what the business is or will be doing on a day-to-day basis. References: OMG - BMM - Mission |
 Mission
Mission |
A Mission indicates the ongoing operational activity of the enterprise. The Mission describes what the business is or will be doing on a day-to-day basis. References: OMG - BMM - Mission |
 Objective Objective |
An Objective is a statement of an attainable, time-targeted, and measurable target that the enterprise seeks to meet in order to achieve its Goals. References: OMG - BMM - Objective |
||
 Organization Unit Organization Unit |
Organization Unit has two roles: 1. It is a concept in the Business Motivation Model, participating in the following associations: • defines Ends, • establishes Means, • makes Assessments, • recognizes Influencers, • may be defined by a Strategy, and • may be responsible for Business Processes. The BPMN concept ‘performer,’ which can be a specific individual, a group, an organization role or position, or an organization, is the BMM concept of an organization unit in the roles of being responsible for activities in an organization. 2. It is usually the basis for defining the boundaries of the enterprise being modeled. The decomposition of Business Policies, Courses of Action, and Desired Results and assignment of responsibilities within the enterprise is often guided by (or, at least, consistent with) the definition of units within the organization structure. References: OMG - BMM - Organizational Unit |
 Organization
Organization |
An Organization is a group of people who share a common purpose and establish a functional division of labor in pursuit of their common purpose. It is the relationships between its members in the pursuit of their common purpose that give unity and identity to an organization. References: OMG - BMM - Organizational Unit OMG - UAF - ActualOrganization OpenGroup - ArchiMate - Business Internal Active Structure Element Russell Ackoff - System of concepts - FunctionalDivisionOfLabor Russell Ackoff - System of Concepts - Organizations Russell Ackoff - Transformational leadership - Social System SAFe© - Organizational Agility |
 Strategy Strategy |
A Strategy is one component of the plan for the Mission. A Strategy represents the essential Course of Action to achieve Ends (Goals in particular). A Strategy usually channels efforts towards those Goals. A Strategy is more than simply a resource, skill, or competency that the enterprise can call upon; rather, a Strategy is accepted by the enterprise as the right approach to achieve its Goals, given the environmental constraints and risks. References: OMG - BMM - Strategy |
 Strategy
Strategy |
A Strategy is one component of the plan for the Mission. A Strategy represents the essential Course of Action to achieve Ends (Goals in particular). A Strategy usually channels efforts towards those Goals. A Strategy is more than simply a resource, skill, or competency that the enterprise can call upon; rather, a Strategy is accepted by the enterprise as the right approach to achieve its Goals, given the environmental constraints and risks. (From BMM). References: OMG - BMM - Strategy |
 Tactic Tactic |
A Tactic is a Course of Action that represents part of the detailing of Strategies. A Tactic implements Strategies. For example, the Tactic “Call first-time customers personally” implements the Strategy “Increase repeat business.” Tactics generally channel efforts towards Objectives. For example, the Tactic “Ship products for free” channels efforts towards the Objective “Within six months, 10% increase in product sales.” References: OMG - BMM - Tactic |
 Tactic
Tactic |
A Tactic is a Course of Action that represents part of the detailing of Strategies. A Tactic implements Strategies. For example, the Tactic “Call first-time customers personally” implements the Strategy “Increase repeat business.” Tactics generally channel efforts towards Objectives. For example, the Tactic “Ship products for free” channels efforts towards the Objective “Within six months, 10% increase in product sales.” References: OMG - BMM - Tactic |
 Vision Vision |
A Vision describes the future state of the enterprise, without regard to how it is to be achieved. A Vision is the ultimate, possibly unattainable, state the enterprise would like to achieve. |
 Vision
Vision |
A Vision describes the future state of the enterprise, without regard to how it is to be achieved. A Vision is the ultimate, possibly unattainable, state the enterprise would like to achieve. |
EXTERNAL REFERENCES
| Framework reference | SysFEAT Description |
|---|---|
 OMG - BMM - Assessment OMG - BMM - Assessment |
An Assessment is a judgment of some Influencer that affects the organization’s ability to employ its Means or achieve its Ends. In other words, an Assessment expresses a logical connection (i.e., fact type) between Influencers and the Ends and/ or Means of the business plans. In this way, an Assessment indicates which Influencers are relevant to which Ends and/or Means. |
 OMG - BMM - Business Policy OMG - BMM - Business Policy |
 Business Policy
Business PolicyA Business Policy is a Policy that is not directly enforceable whose purpose is to govern or guide the enterprise. A Business Policy is a Directive that is not directly enforceable8 whose purpose is to govern or guide the enterprise. Business Policies provide the basis for Business Rules. Business Policies also govern Business Processes  Policy
PolicyA Policy is a Directive that is not directly enforceable whose purpose is to govern, guide or constrain the structure and Behavior Type of Agent Types in the enterprise. Policies provide the basis for rules and govern Behavior Types carried out by Agent Types. |
 OMG - BMM - Business Process OMG - BMM - Business Process |
Business Processes realize Courses of Action. They provide processing steps, sequences (including cycles, branches, and synchronization), structure (decomposition and reuse), interactions, and connection to events that trigger the processes. Courses of Action are governed by Business Policies; Business Processes are also governed by Business Policies.  Business Process
Business ProcessA Business Process is a set of Business-Process Steps performed by Org-Unit Types and/or by automated systems (Business Systems) to produce a Business Outcome Event. It is depicted as a series of Business-Process Steps, controlled by Business Events and conditions. Business-Process Steps are carried out by the involvment of Org-Unit Types and system resources (often Applications) as participants in the process (Participant Business Agents). During its course of action, a Business Process consumes or produces Business Objects. 1) It may memorize or access Business Objects from its Process Store. 2) It may receive Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Consumption. 3) It may signal the production of Business Objects at its boundary: Business Outcome Production. The course of actions of a Business Process is constrained by the application of rules ( Business Rule Enforcement) that define how to react to what is allowed and not allowed to do, |
 OMG - BMM - Business Rule OMG - BMM - Business Rule |
 Behavioral Rule
Behavioral RuleA Behavioral Rule is a Directive intended to guide the Behavior of Agent Types, in compliance with enterprise Policy(ies) or regulations. Often, a Behavioral Rule is derived from a Policy. Behavioral Rules are enforced in Processes and Agent Types.  Business Resource Rule
Business Resource RuleA Business Resource Rule is a Resource Rule that is enforced by Business Operating Assets of the Enterprise. Business Rules provide specific, practicable guidance to implement Business Policies. Some Business Rules could be automated in software; some are practicable only by people.  Conceptual Business Rule
Conceptual Business RuleA Conceptual Business Rule is a rule that is under business jurisdiction. A rule’s being 'under business jurisdiction' means that it is under the jurisdiction of the semantic community that it governs or guides - that the semantic community can opt to change or discard the rule. Laws of physics may be relevant to a company (or other semantic community); legislation and regulations may be imposed on it; external standards and best Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Business Rules, v1.0 161 practices may be adopted. These things are not business rules from the company’s perspective, since it does not have the authority to change them. The company will decide how to react to laws and regulations, and will create business rules to ensure compliance with them. Similarly, it will create business rules to ensure that standards or best practices are implemented as intended. |
 OMG - BMM - Common Vocabulary OMG - BMM - Common Vocabulary |
|
 OMG - BMM - Course of Action OMG - BMM - Course of Action |
A Course of Action is an approach or plan for configuring some aspect of the enterprise involving things, processes, locations, people, timing, or motivation undertaken to achieve Desired Results. In other words, a Course of Action channels efforts towards Desired Results. To help ensure success in this regard, Courses of Action are governed by Directives.  Course of Action
Course of ActionA plan recognized by an enterprise as being essential to achieving its goals - i.e. a strategic specification of what the enterprise does. In other words, a Course of Action channels efforts towards Desired Results. Business Capabilities might be required by an Enterprise to conduct its Courses of Action. |
 OMG - BMM - Directive OMG - BMM - Directive |
 Directive
DirectiveA Directive is an authoritative declaration that indicates how Agents and their Behaviors should be (or should not be) in the enterprise. Specifically, a Directive defines, constrains or liberates some aspects of an Agent and its Behaviors. As such, Directives shall be considered as constraning Asset Propertys. Directives are intended to assert agent structures or to control or influence their Behaviors. Directives are stated in declarative form. As the name suggests, Directives indicate how the Courses of Action should, or should not, be carried out (in other words, they govern Courses of Action). Specifically, a Directive defines or constrains or liberates some aspect of an enterprise. It is intended to assert business structure or to control or influence the behavior of the business, and is stated in declarative form. The Policies domain defines Directives and Behavioral Rules that constrain enterprise structures (Agent Types structure) and Behavior Types. |
 OMG - BMM - External Influencer OMG - BMM - External Influencer |
 Exogenous Driver
Exogenous DriverAn Exogenous Driver is an external Driver whose source of change is outside the enterprise’s organizational boundaries and that can impact its employment of Means or achievement of Ends. An influencer that is outside the enterprise’s organizational boundaries. |
 OMG - BMM - Goal OMG - BMM - Goal |
 Enterprise Goal
Enterprise GoalAn Enterprise Goal is an ideal target Value Proposition that tends to be longer term, and is defined qualitatively rather than quantitatively. It should be sufficiently narrow-focused so that Objectives can be defined for it. A Goal is a statement about a state or condition of the enterprise to be brought about or sustained through appropriate Means. A Goal amplifies a Vision; that is, it indicates what must be satisfied on a continuing basis to effectively attain the Vision. |
 OMG - BMM - Influencer OMG - BMM - Influencer |
 Driver
DriverA Driver is a factor which can have a significant impact on the activities, and goals of an Enterprise or a Management System. An Influencer is something that can cause changes that affect the enterprise in its employment of its Means or achievement of its Ends. Alternatively, it might confirm that there are no changes where changes might have been expected. |
 OMG - BMM - Internal Influencer OMG - BMM - Internal Influencer |
 Endogenous Driver
Endogenous DriverEndogenous Drivers are those which subject of concern are within an enterprise that can impact its employment of Means or achievement of Ends. An influencer from within the enterprise. |
 OMG - BMM - Mission OMG - BMM - Mission |
 Mission
MissionA Mission indicates the ongoing operational activity of the enterprise. The Mission describes what the business is or will be doing on a day-to-day basis. A Mission indicates the ongoing operational activity of the enterprise. The Mission describes what the business is or will be doing on a day-to-day basis. |
 OMG - BMM - Objective OMG - BMM - Objective |
 Enterprise Objective
Enterprise ObjectiveBusiness Capability that is exhibited by an Enterprise Stage with quantified measure (KPI) and potential geopolitical scope (Site) for a defined market segment (Business Partner). An Enterprise Objective is a quantifiable end that a company/organization wants to achieve for a given Enterprise Initiative. An Enterprise Objective may support an Enterprise Goal; it may be refined into sub-objectives. An Enterprise Objective may concern a defined Exhibited Capability and be addressed by a defined Tactic. An Objective is a statement of an attainable, time-targeted, and measurable target that the enterprise seeks to meet in order to achieve its Goals. |
 OMG - BMM - Organizational Unit OMG - BMM - Organizational Unit |
 Organization
OrganizationAn Organization is a group of people who share a common purpose and establish a functional division of labor in pursuit of their common purpose. It is the relationships between its members in the pursuit of their common purpose that give unity and identity to an organization. Organization Unit has two roles: 1. It is a concept in the Business Motivation Model, participating in the following associations: • defines Ends, • establishes Means, • makes Assessments, • recognizes Influencers, • may be defined by a Strategy, and • may be responsible for Business Processes. The BPMN concept ‘performer,’ which can be a specific individual, a group, an organization role or position, or an organization, is the BMM concept of an organization unit in the roles of being responsible for activities in an organization. 2. It is usually the basis for defining the boundaries of the enterprise being modeled. The decomposition of Business Policies, Courses of Action, and Desired Results and assignment of responsibilities within the enterprise is often guided by (or, at least, consistent with) the definition of units within the organization structure. |
 OMG - BMM - Strategy OMG - BMM - Strategy |
A Strategy is one component of the plan for the Mission. A Strategy represents the essential Course of Action to achieve Ends (Goals in particular). A Strategy usually channels efforts towards those Goals. A Strategy is more than simply a resource, skill, or competency that the enterprise can call upon; rather, a Strategy is accepted by the enterprise as the right approach to achieve its Goals, given the environmental constraints and risks.  Strategy
Strategy A Strategy is one component of the plan for the Mission. A Strategy represents the essential Course of Action to achieve Ends (Goals in particular). A Strategy usually channels efforts towards those Goals. A Strategy is more than simply a resource, skill, or competency that the enterprise can call upon; rather, a Strategy is accepted by the enterprise as the right approach to achieve its Goals, given the environmental constraints and risks. (From BMM). |
 OMG - BMM - Tactic OMG - BMM - Tactic |
A Tactic is a Course of Action that represents part of the detailing of Strategies. A Tactic implements Strategies. For example, the Tactic “Call first-time customers personally” implements the Strategy “Increase repeat business.” Tactics generally channel efforts towards Objectives. For example, the Tactic “Ship products for free” channels efforts towards the Objective “Within six months, 10% increase in product sales.”  Tactic
TacticA Tactic is a Course of Action that represents part of the detailing of Strategies. A Tactic implements Strategies. For example, the Tactic “Call first-time customers personally” implements the Strategy “Increase repeat business.” Tactics generally channel efforts towards Objectives. For example, the Tactic “Ship products for free” channels efforts towards the Objective “Within six months, 10% increase in product sales.” |